Pipe Support Anchor, Directional Anchor, Guide, Shoe
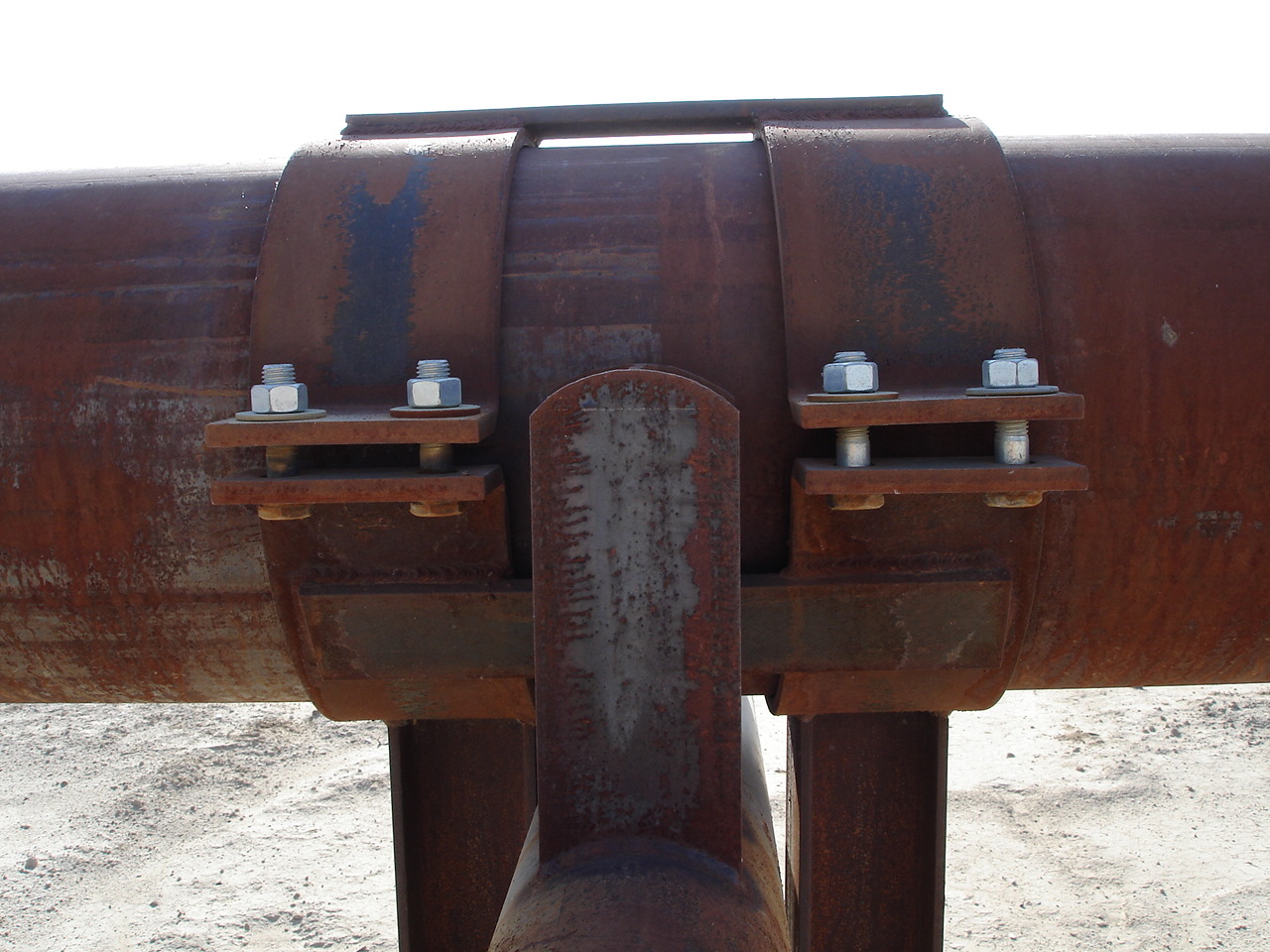
Pipe Support "Anchor"
A pipe support anchor is a device or component used in engineering and construction to restrain the movement of a pipe or pipeline system. It is designed to prevent axial movement, which refers to movement along the length of the pipe. Axial movement can occur due to factors such as thermal expansion and contraction, pressure changes, vibrations, and external forces. The primary purpose of a pipe support anchor is to maintain the integrity and stability of the pipeline by preventing excessive movement that could lead to stress, deformation, or even failure of the piping system. Pipe support anchors are strategically placed along the length of the pipeline, typically at specific intervals, to provide effective restraint against axial movement.
Key Points about Pipe Support "Anchor"
Design - Pipe support anchors are designed to withstand the forces generated by the movement of the pipe. They are engineered to handle the anticipated thermal expansion and contraction of the pipe, as well as any other loads that the pipeline may experience.
Material - They are typically made from materials that can withstand the operating conditions of the pipeline, including the temperature, pressure, and environmental factors. Common materials include steel, stainless steel, and other high strength alloys.
Installation - Proper installation of pipe support anchors is crucial to their effectiveness. They must be securely attached to the structure or foundation that the pipeline is mounted on. The anchor design should consider factors such as the layout of the pipeline, its routing, and any potential movement points.
Guidance - In some cases, pipe support anchors may also incorporate features that help guide the pipe's movement, particularly when thermal expansion or contraction occurs. This can prevent the pipe from buckling or experiencing excessive stress.
Expansion Joints - In situations where a pipe needs to expand or contract significantly due to temperature changes, expansion joints are often used in conjunction with pipe support anchors. Expansion joints allow controlled movement while the anchors prevent uncontrolled axial movement.
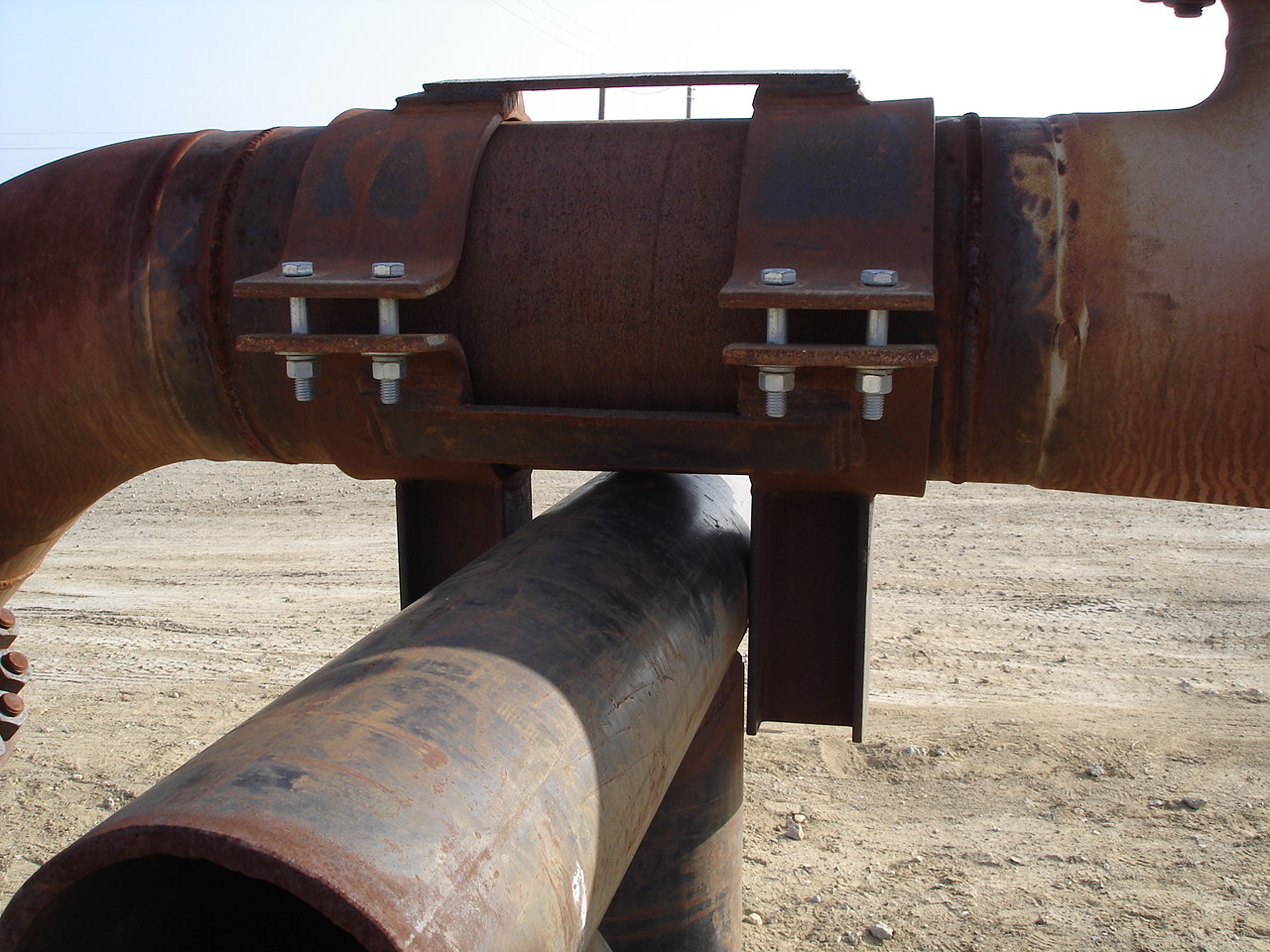
Pipe Support "Directional Anchor"
A pipe support directional anchor is a component used in engineering and construction to restrict or control the movement of a pipe or pipeline system in a specific direction. Unlike a regular pipe support anchor that primarily prevents axial movement (movement along the length of the pipe), a directional anchor focuses on preventing movement perpendicular to the pipe's axis. This type of movement is often referred to as lateral movement or transverse movement. The primary purpose of a pipe support directional anchor is to ensure that the pipe remains stable and properly aligned, especially when subjected to external forces, such as wind loads, seismic activity, and vibrations. These external forces could potentially cause the pipe to sway, bend, or move out of its intended position, which could lead to structural issues or operational problems.
Key Points about Pipe Support "Directional Anchors"
Restriction - The primary function of a directional anchor is to restrict the lateral movement of the pipe. It does this by providing a point of resistance against forces that might push or pull the pipe in a direction perpendicular to its length.
Stability - Directional anchors contribute to the overall stability of the pipeline system. By preventing lateral movement, they help maintain the alignment of the pipes, which is crucial for the efficient and safe functioning of the system.
External Forces - These anchors are particularly important in situations where the pipeline is exposed to external forces that could cause movement. For example, in earthquake prone areas or locations with strong winds, directional anchors play a key role in preventing excessive pipe movement.
Installation - Proper installation is critical to the effectiveness of directional anchors. They must be securely attached to the structure or foundation supporting the pipeline, and their placement should be based on the anticipated forces and directions of movement.
Design - Like other pipe support components, the design of directional anchors considers the materials used, the expected loads, and the conditions of the pipeline environment.
Pipe Support "Guide"
A pipe support guide, also called pipe guide, is a component used in engineering and construction to control and guide the movement of a pipe or pipeline system along a specific path. Pipe guides are designed to prevent lateral movement (movement perpendicular to the pipe's axis) and maintain the alignment of the pipe, particularly when the pipe is subjected to expansion or contraction due to temperature changes. The primary purpose of a pipe support guide is to ensure that the pipe follows a predefined trajectory or route, preventing it from buckling, swaying, or moving out of alignment. This is important in situations where pipes are exposed to temperature variations that cause them to expand or contract. If not properly guided, the pipes might exert excessive stress on the supports, fittings, or other components, which could lead to damage or operational issues.
Key Points about Pipe Support "Guides"
Guidance - The main function of a pipe support guide is to provide controlled guidance for the movement of the pipe. It keeps the pipe within a specific alignment and prevents it from deviating from its intended path.
Expansion and Contraction - Pipe support guides are particularly important in cases where the pipeline is subject to significant thermal expansion and contraction. They allow the pipe to move while ensuring that the movement is controlled and doesn't lead to excessive stress.
Alignment - Maintaining proper alignment is crucial for the efficient functioning of the pipeline system. Pipe guides contribute to this by preventing misalignment, which could result in operational inefficiencies or even damage to the pipeline.
Materials and Design - Pipe guides are designed to withstand the forces and conditions the pipeline might experience. They are typically made from durable materials that can handle the environmental and operational demands.
Spacing - Proper spacing between pipe guides is essential for effective guidance. The spacing depends on factors such as the pipe's material, diameter, temperature range, and the forces it will be subjected to.
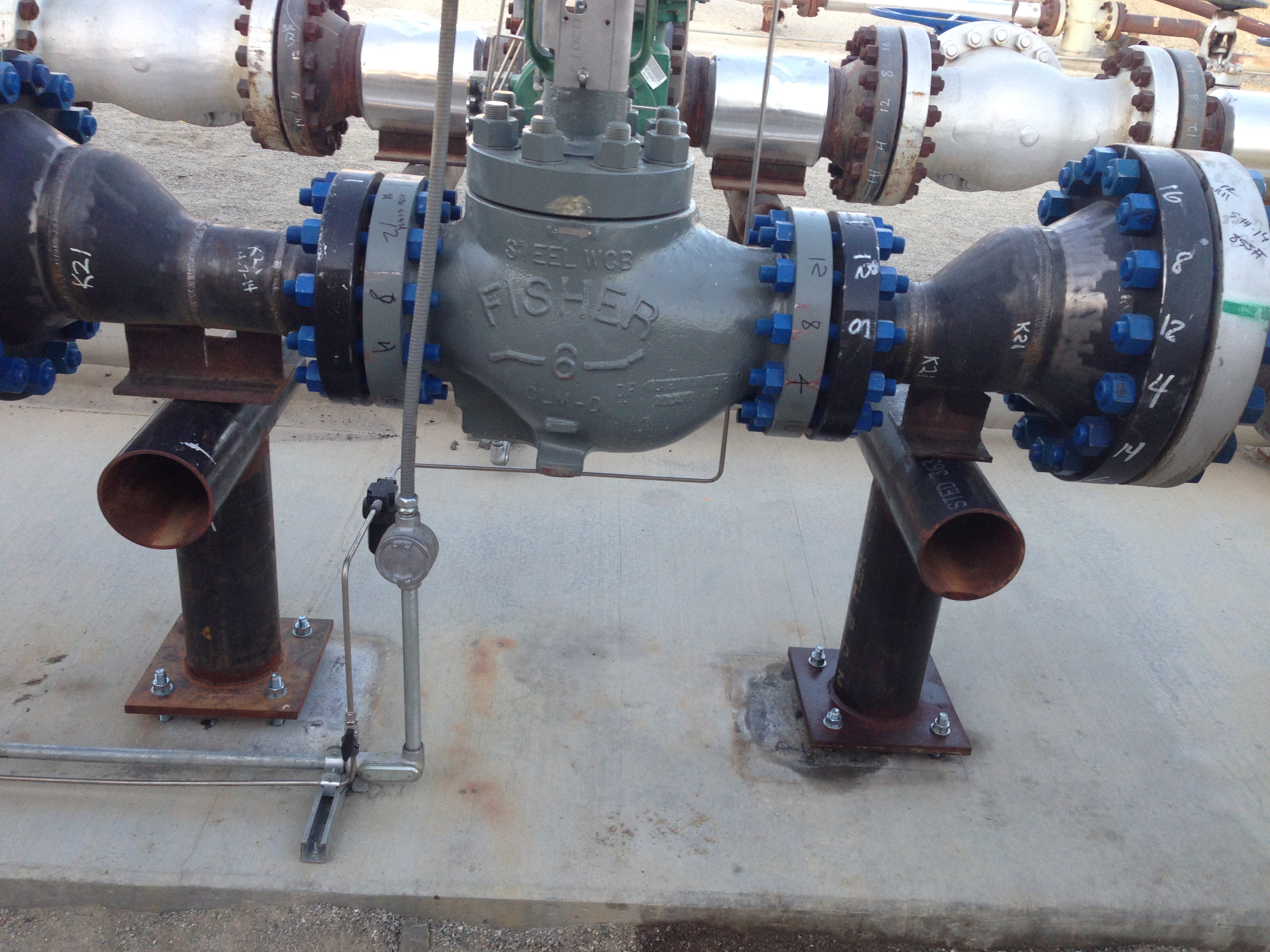

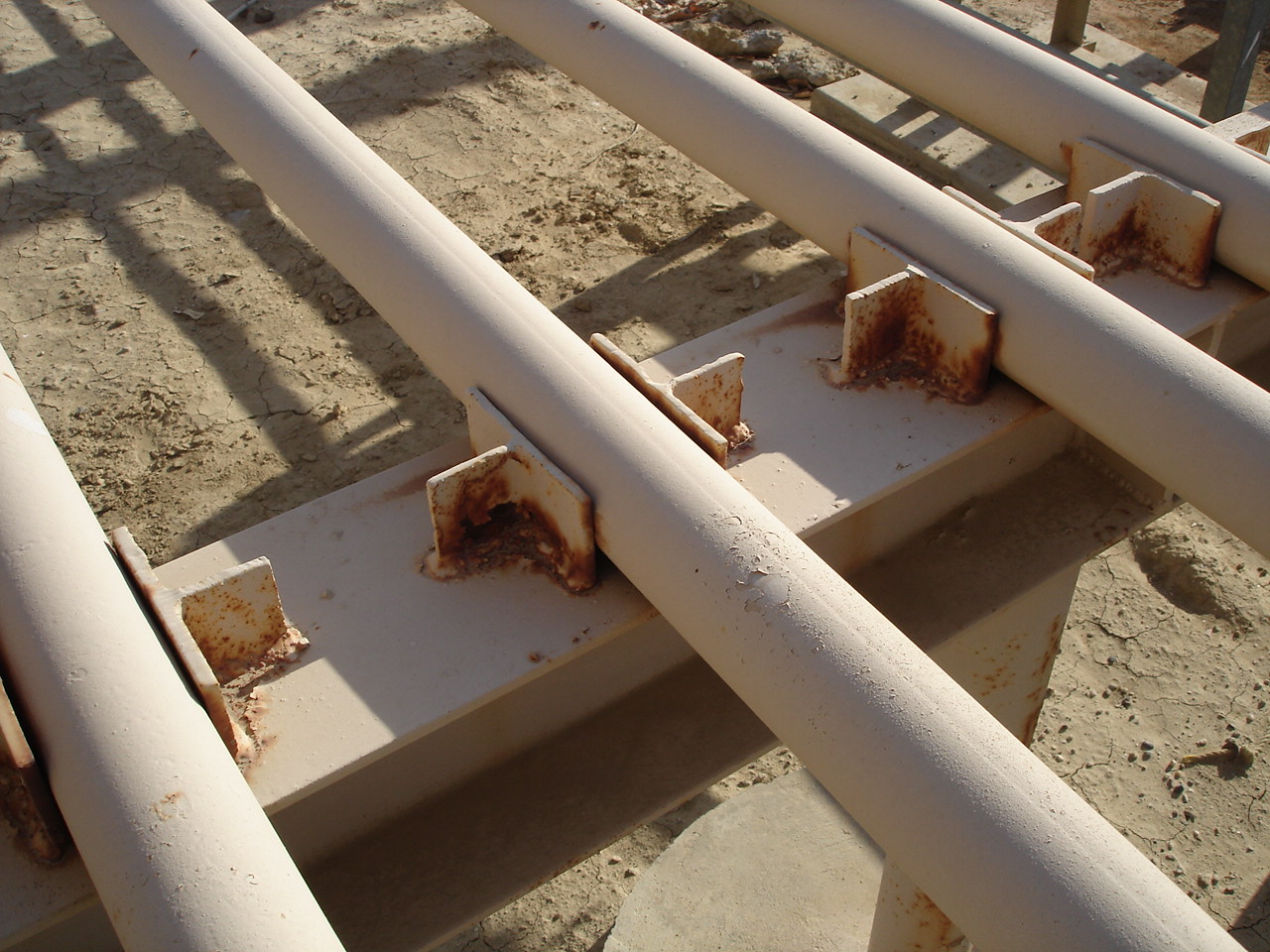
Pipe Support "Shoe"
A pipe support shoe, also called pipe shoe or pipe support cradle, is a component used in engineering and construction to support and bear the weight of a pipe or pipeline system at specific points where the pipe connects to a structure or changes direction. Pipe support shoes are designed to distribute the load of the pipe evenly onto the supporting structure, preventing excessive stress and deformation. The primary purpose of a pipe support shoe is to ensure that the weight of the pipe is adequately carried by the supporting structure without causing localized stress concentrations that could lead to damage or failure of the pipe, its connections, or the surrounding infrastructure.
Key Points about Pipe Support "Shoes"
Load Distribution - Pipe support shoes are designed to evenly distribute the weight of the pipe onto the supporting structure. This helps prevent point loads and ensures that the pipe is properly supported.
Connection Points - Pipe support shoes are often used at critical points where the pipe is attached to a structure, such as at pipe hangers, pipe supports, or any location where the pipe changes direction or elevation.
Material and Design - Pipe support shoes are typically made from materials that can handle the weight of the pipe and the operating conditions of the pipeline. They are engineered to withstand various loads and environmental factors.
Alignment - Pipe support shoes contribute to maintaining the proper alignment of the pipe. By supporting the pipe securely, they help prevent sagging, misalignment, and other issues that could affect the pipeline's performance.
Thermal Expansion - In situations where the pipeline is subject to temperature changes, pipe support shoes work in conjunction with other components to allow controlled movement, such as expansion or contraction, without compromising the structural integrity.
Insulation - In applications where pipes carry fluids at different temperatures, insulation might be needed around the pipe. Pipe support shoes can be designed to accommodate insulation materials while still providing proper support.
- See Article - Pipe Support Dont's
Pipe Cross Member Shoe, Guide, Anchor, Directional Anchor
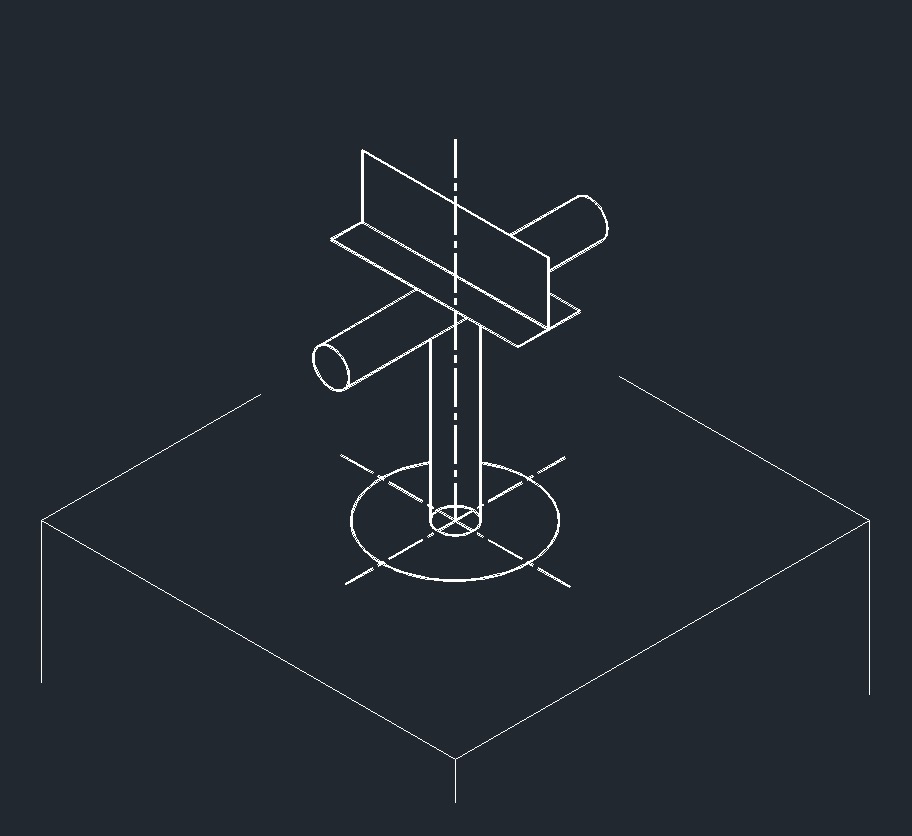 ISO Shoe Left Plane
ISO Shoe Left Plane
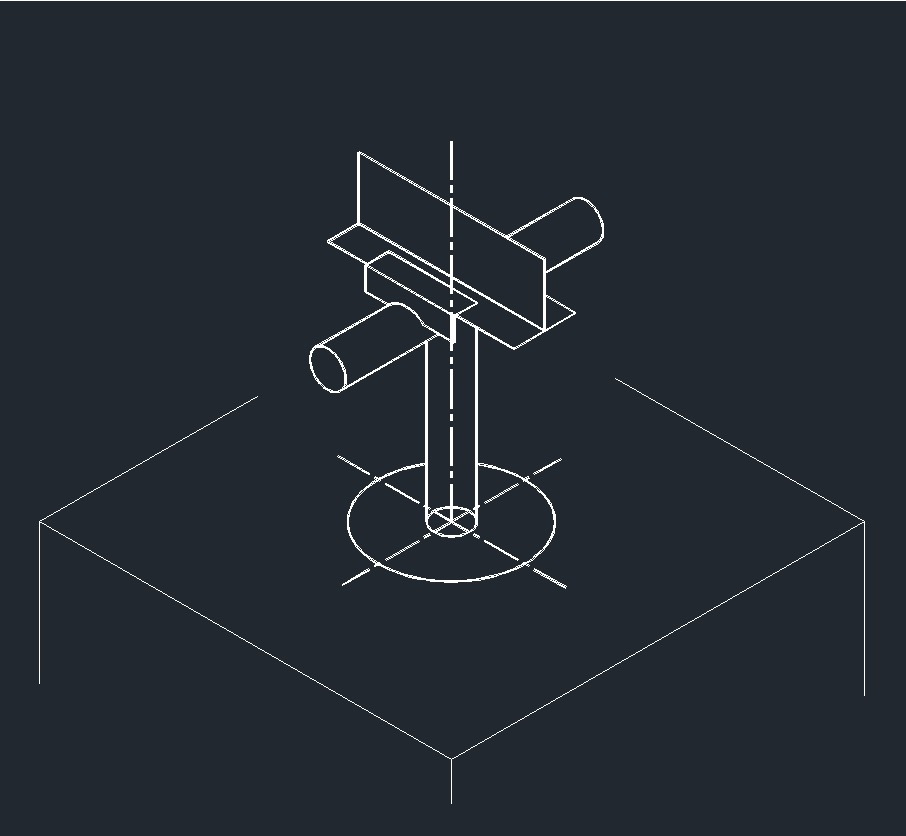 ISO Guide Left Plane
ISO Guide Left Plane
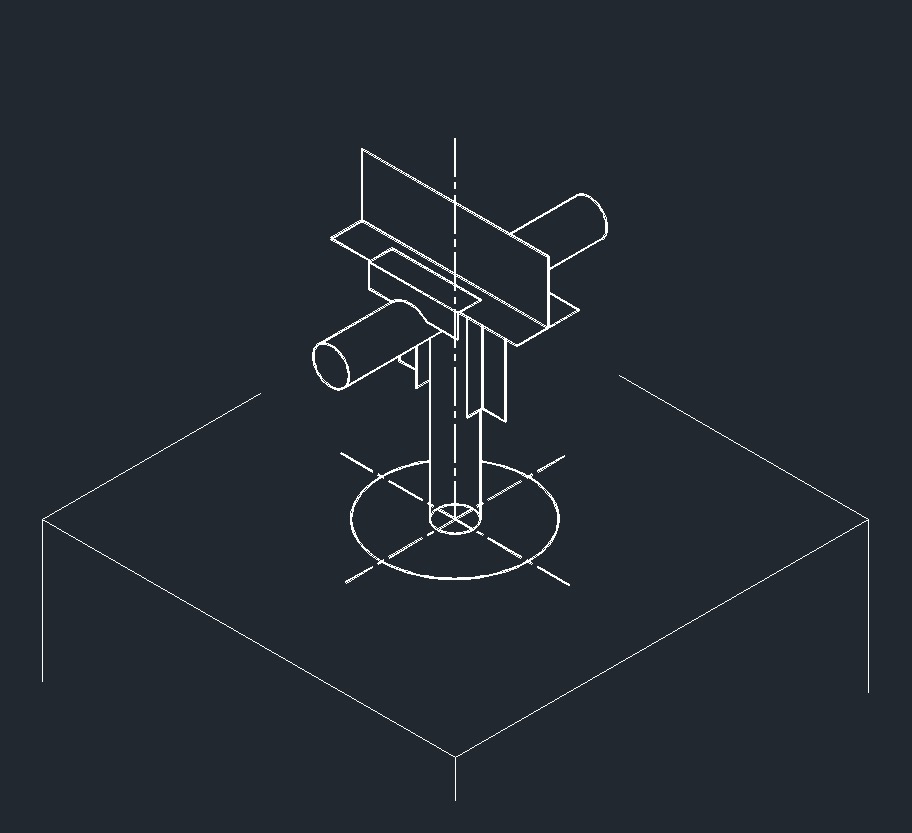 ISO Anchor Left Plane
ISO Anchor Left Plane
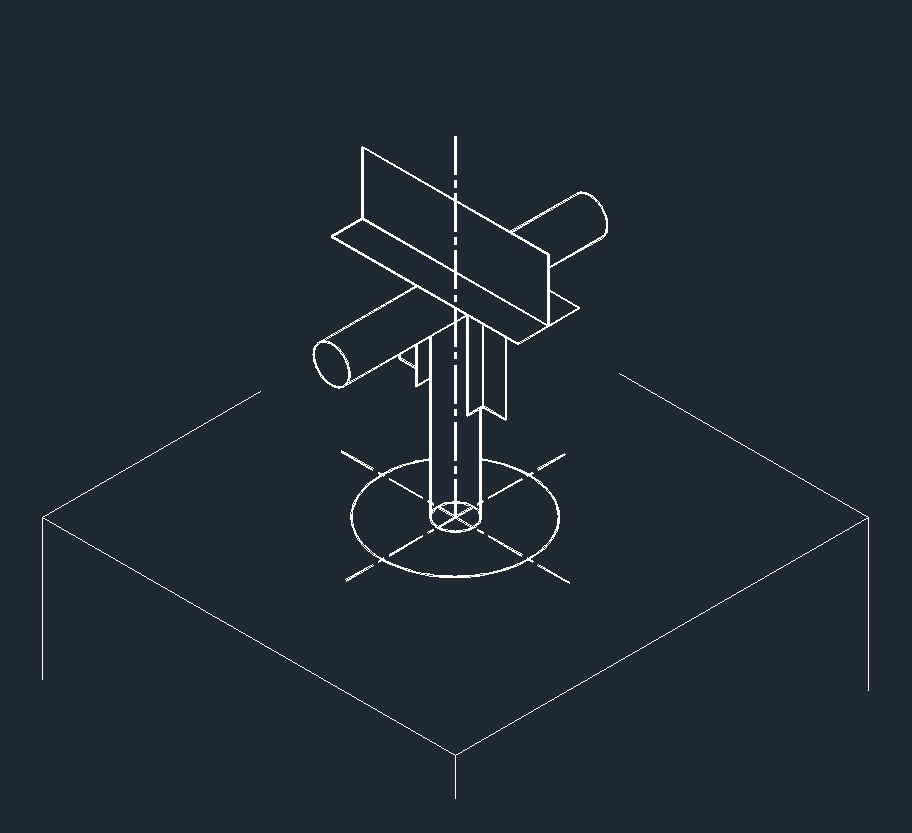 ISO Directional Anchor Left Plane
ISO Directional Anchor Left Plane
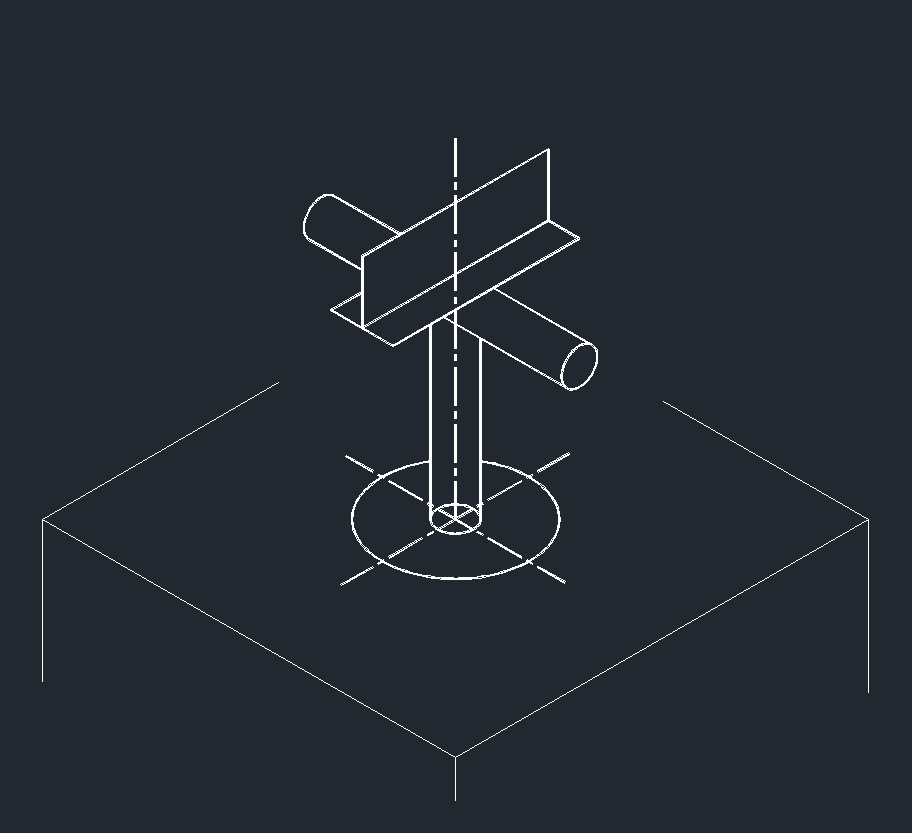 ISO Shoe Right Plane
ISO Shoe Right Plane
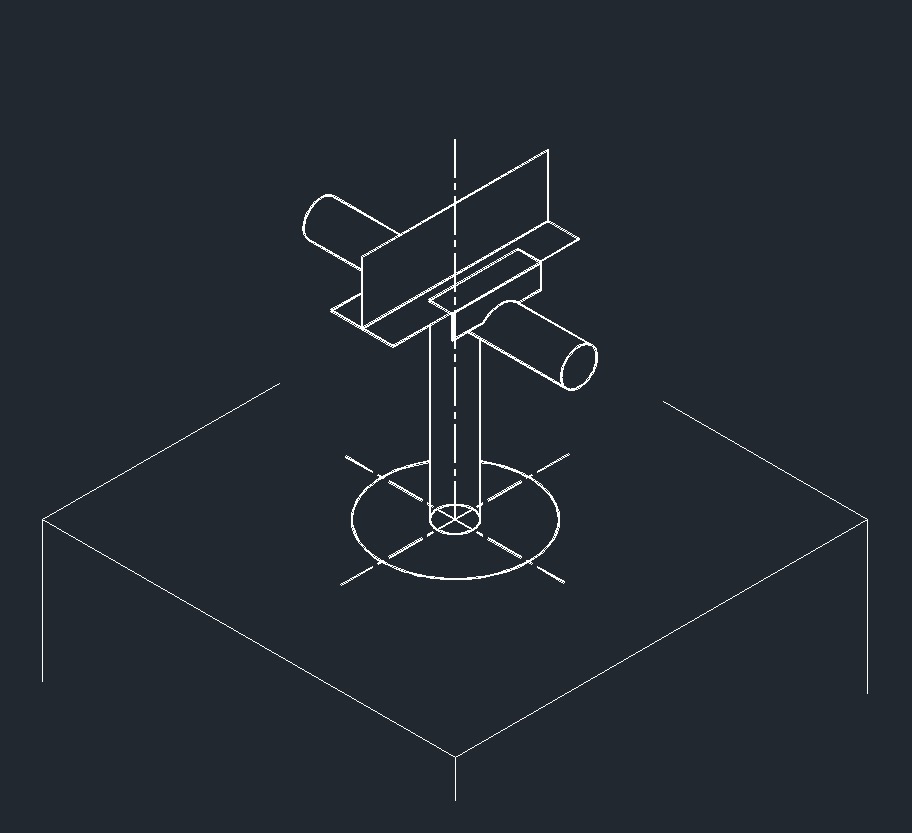 ISO Guide Right Plane
ISO Guide Right Plane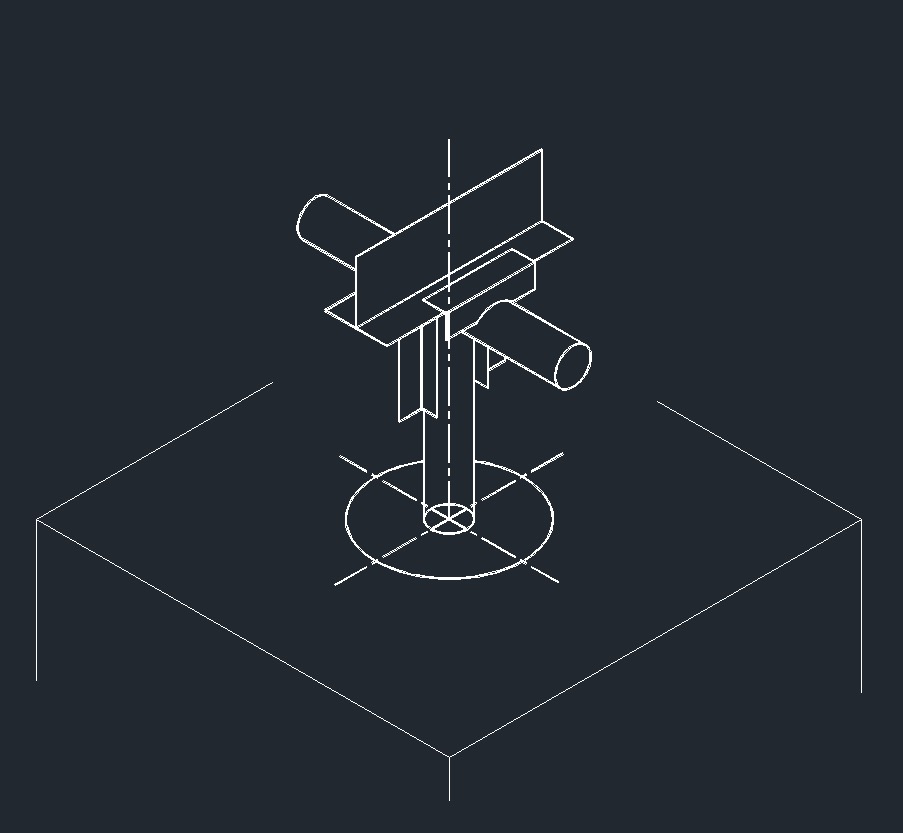 ISO Anchor Right Plane
ISO Anchor Right Plane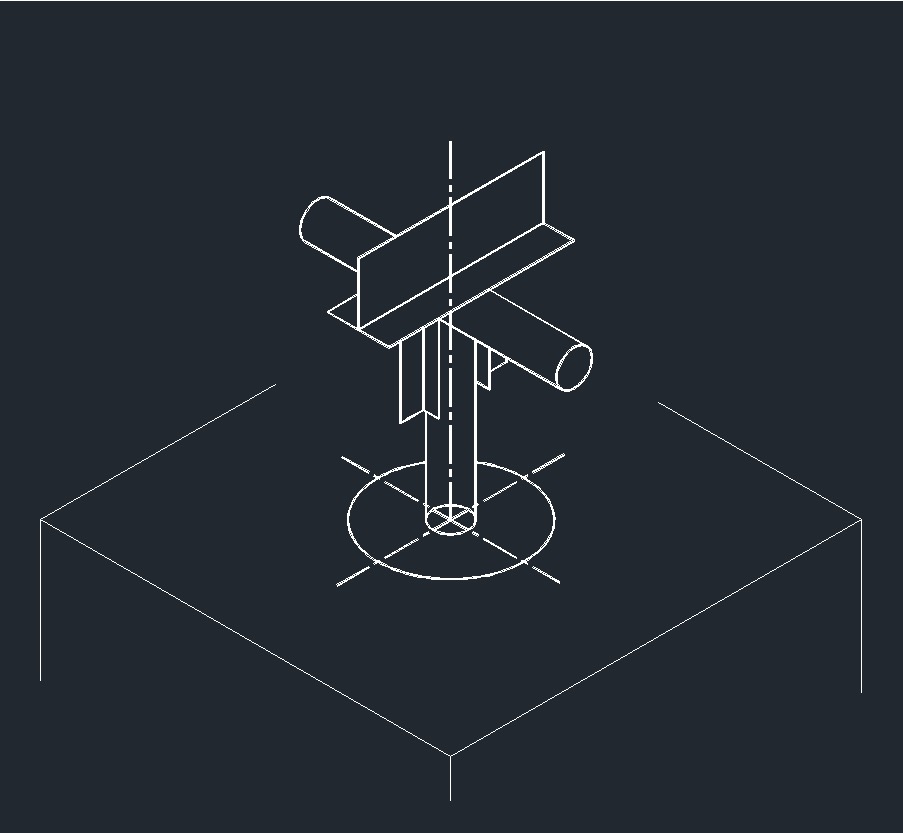 ISO Directional Anchor Right Plane
ISO Directional Anchor Right Plane
Beam Cross Member Shoe, Guide, Anchor, Directional Anchor
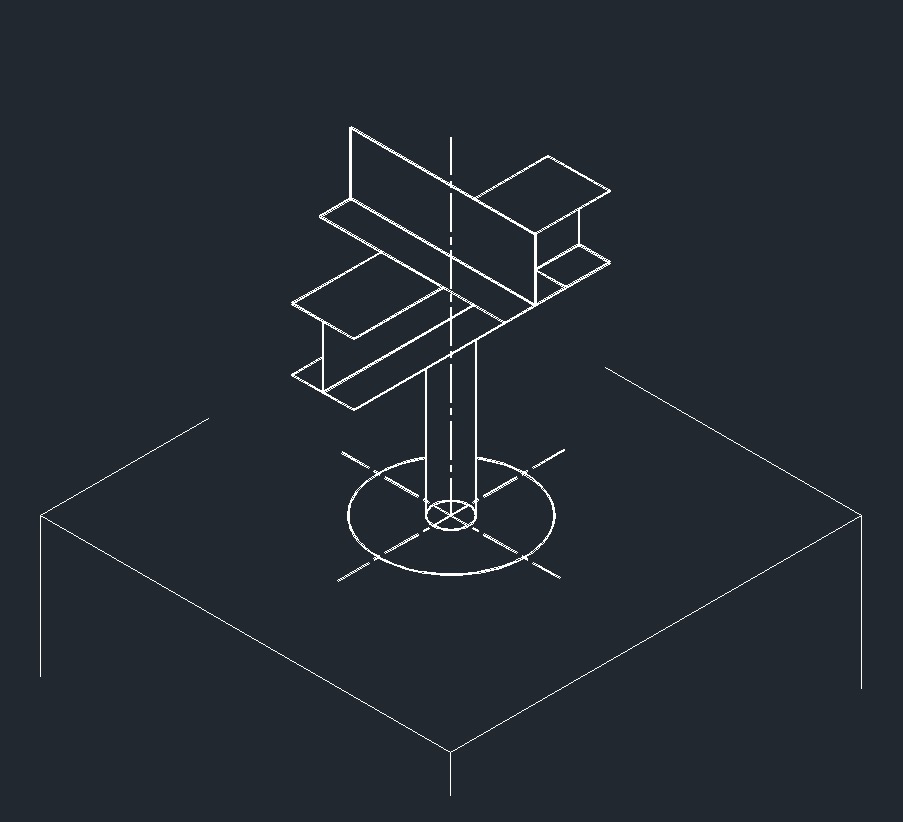 ISO Shoe Left Plane
ISO Shoe Left Plane
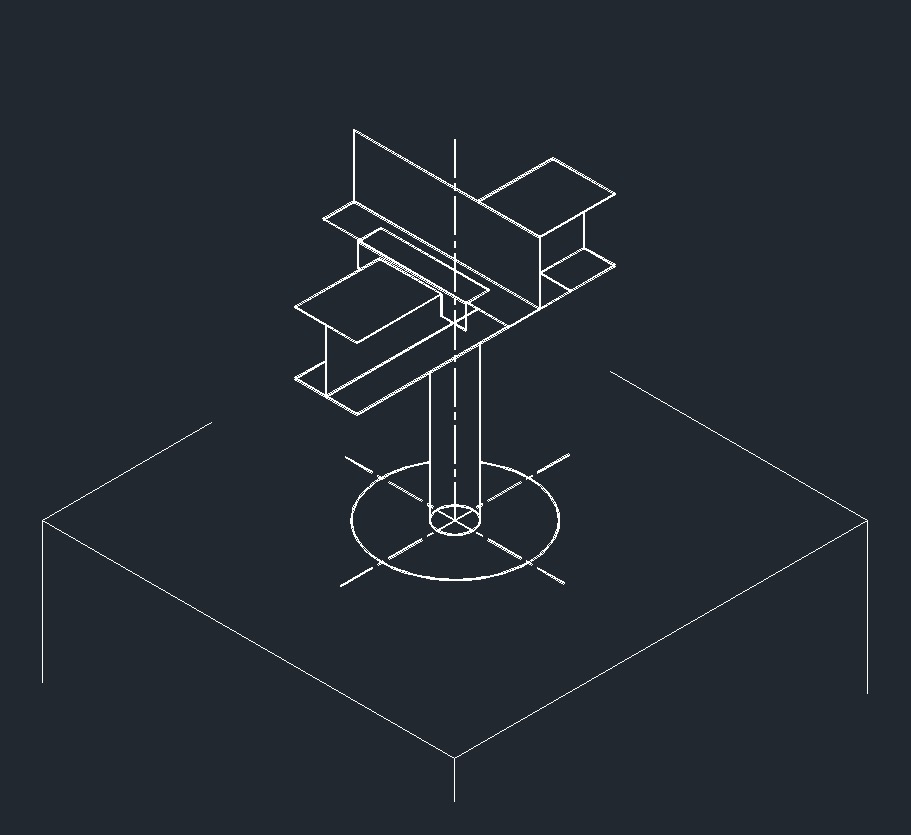 ISO Guide Left Plane
ISO Guide Left Plane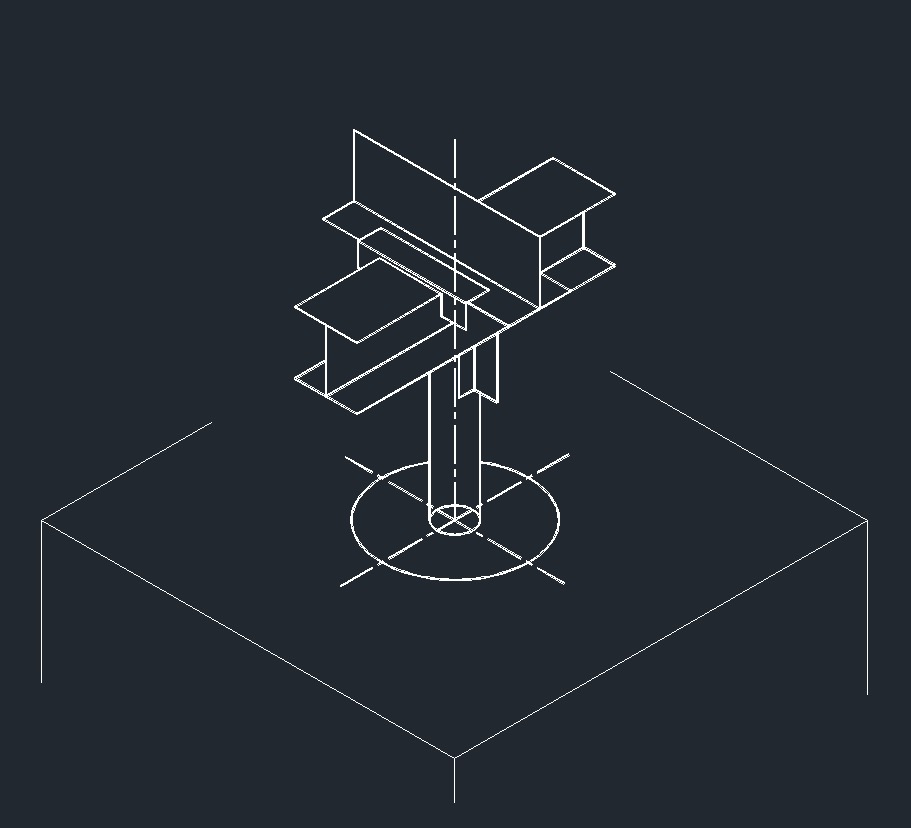 ISO Anchor Left Plane
ISO Anchor Left Plane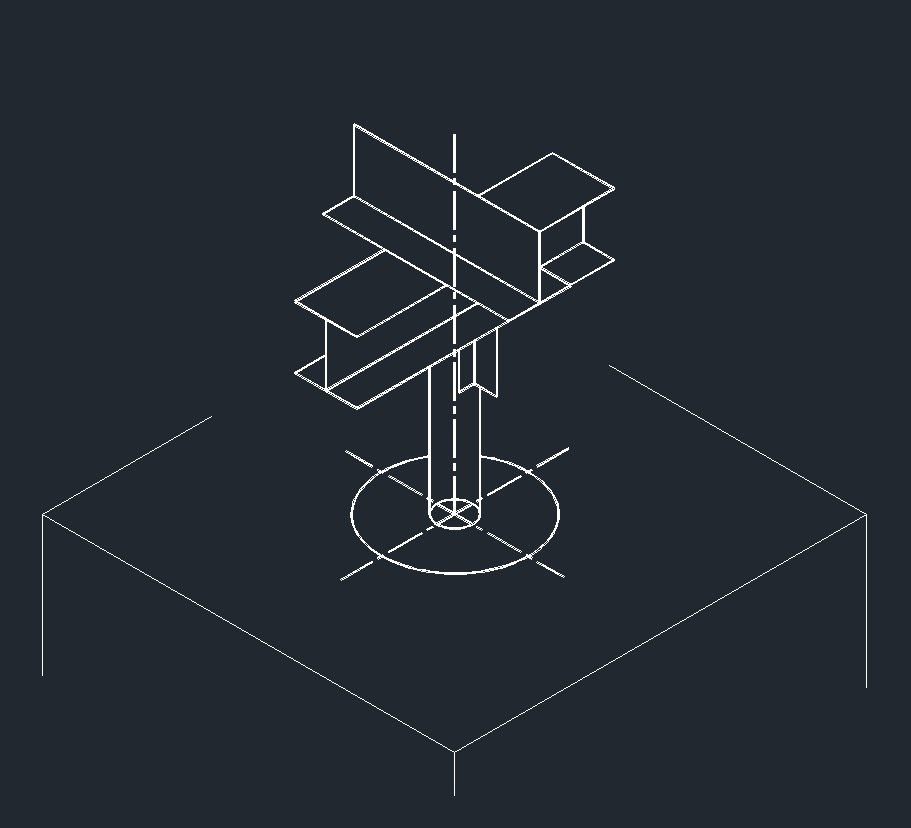 ISO Directional Anchor Left Plane
ISO Directional Anchor Left Plane
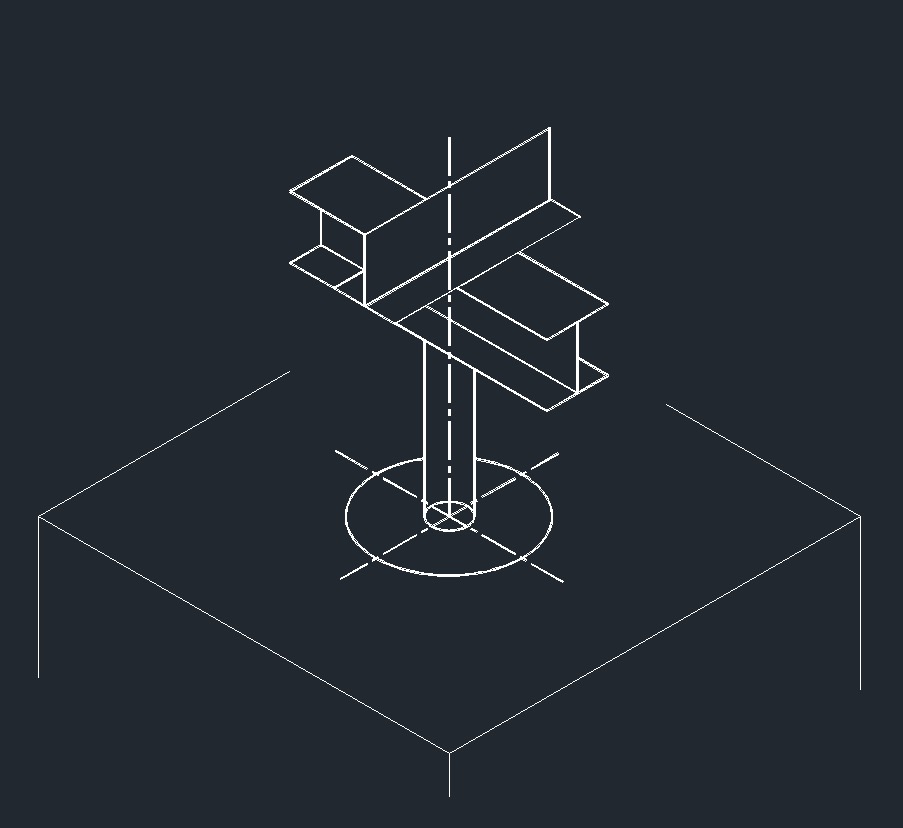 ISO Shoe Right Plane
ISO Shoe Right Plane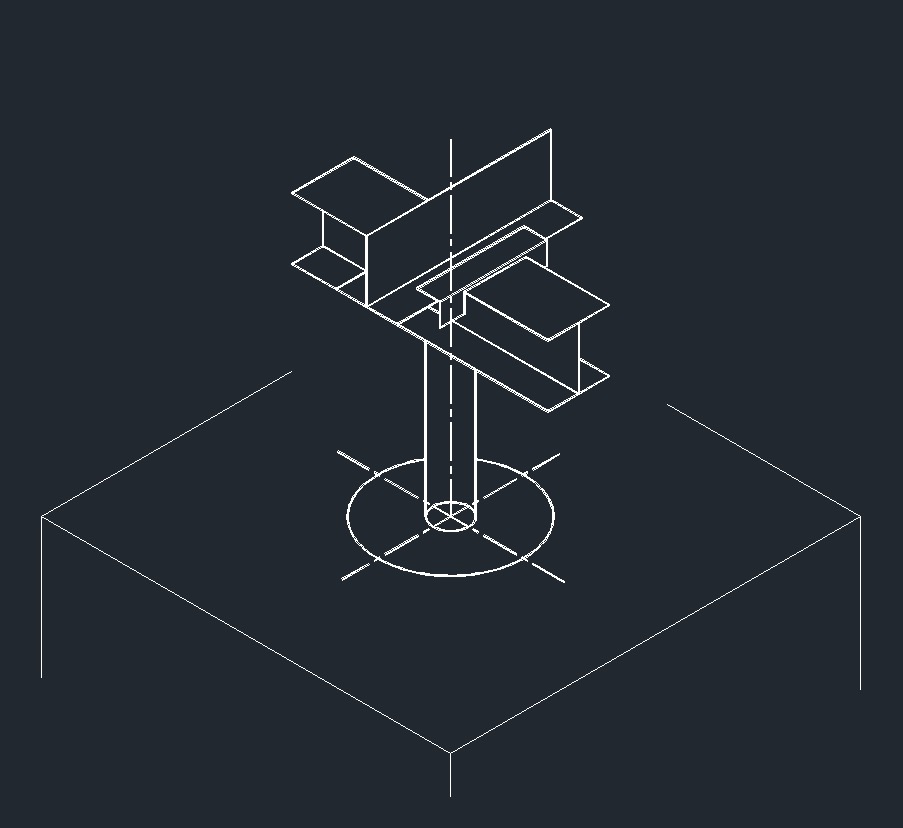 ISO Guide Right Plane
ISO Guide Right Plane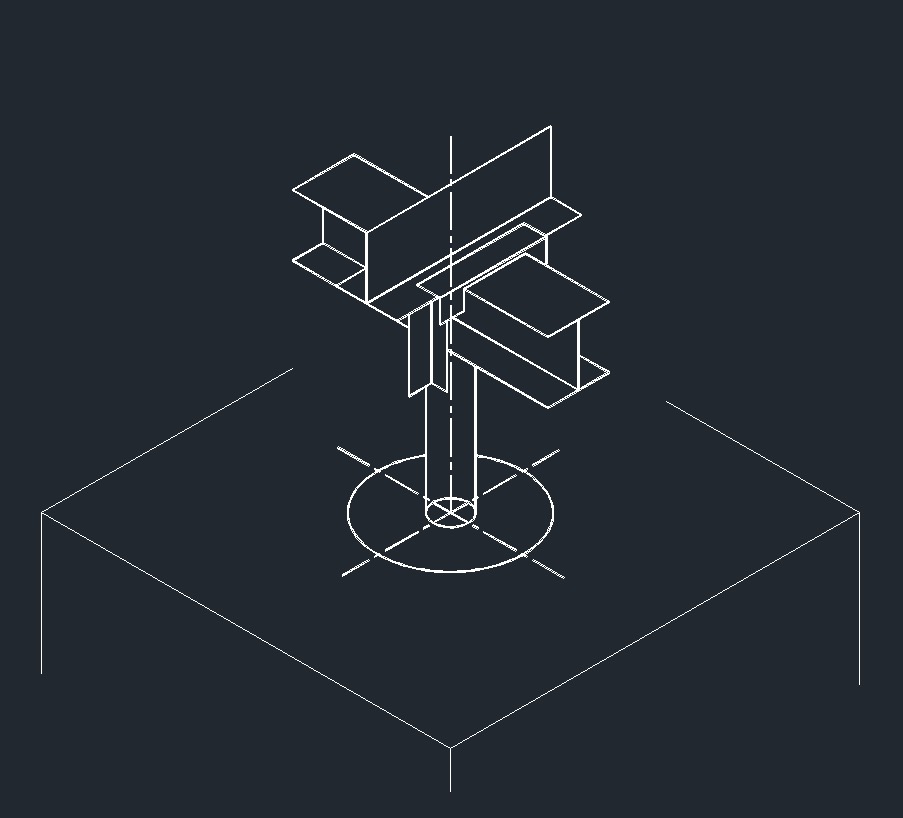 ISO Anchor Right Plane
ISO Anchor Right Plane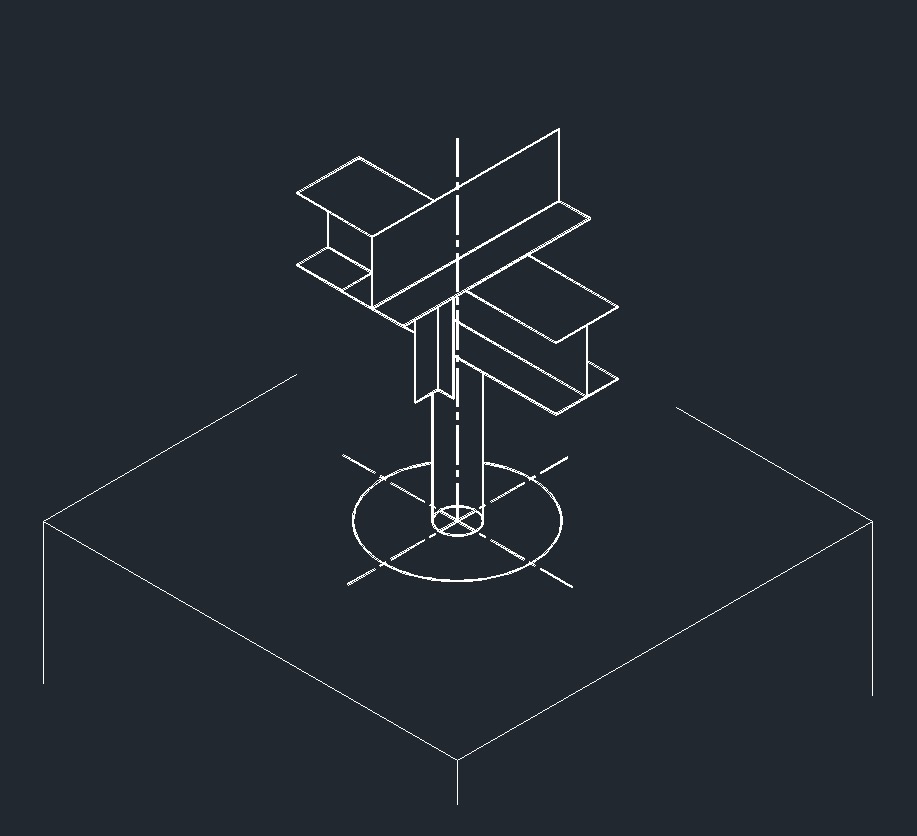 ISO Directional Anchor Right Plane
ISO Directional Anchor Right Plane
Pipe Cross Member Guide, Anchor
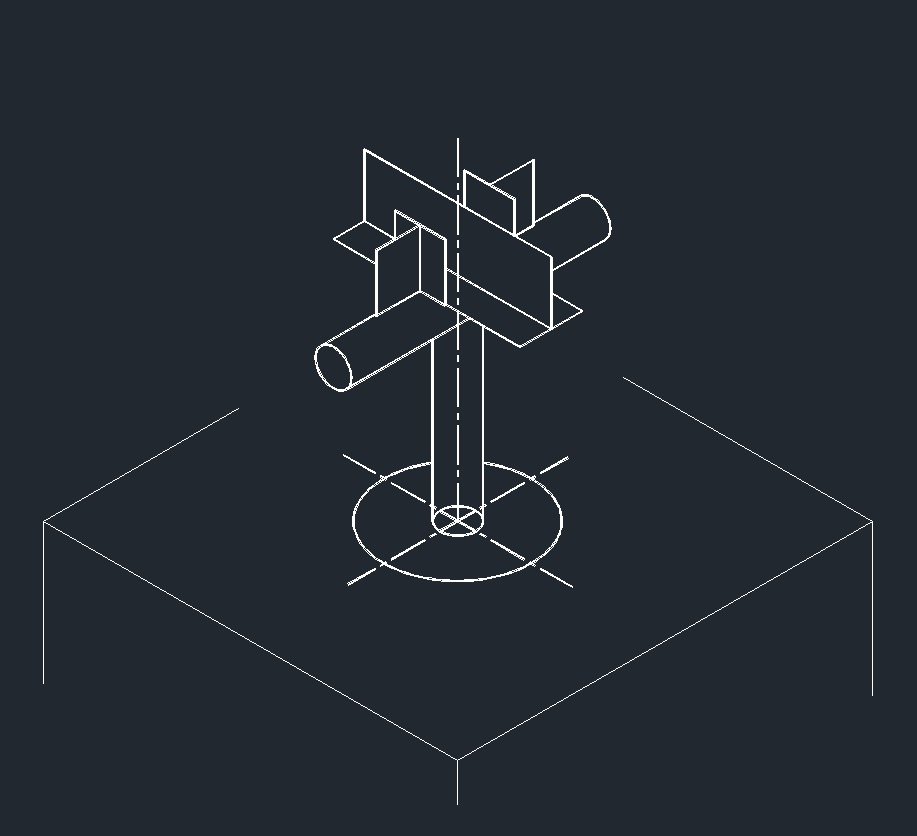 ISO Guide Left Plane
ISO Guide Left Plane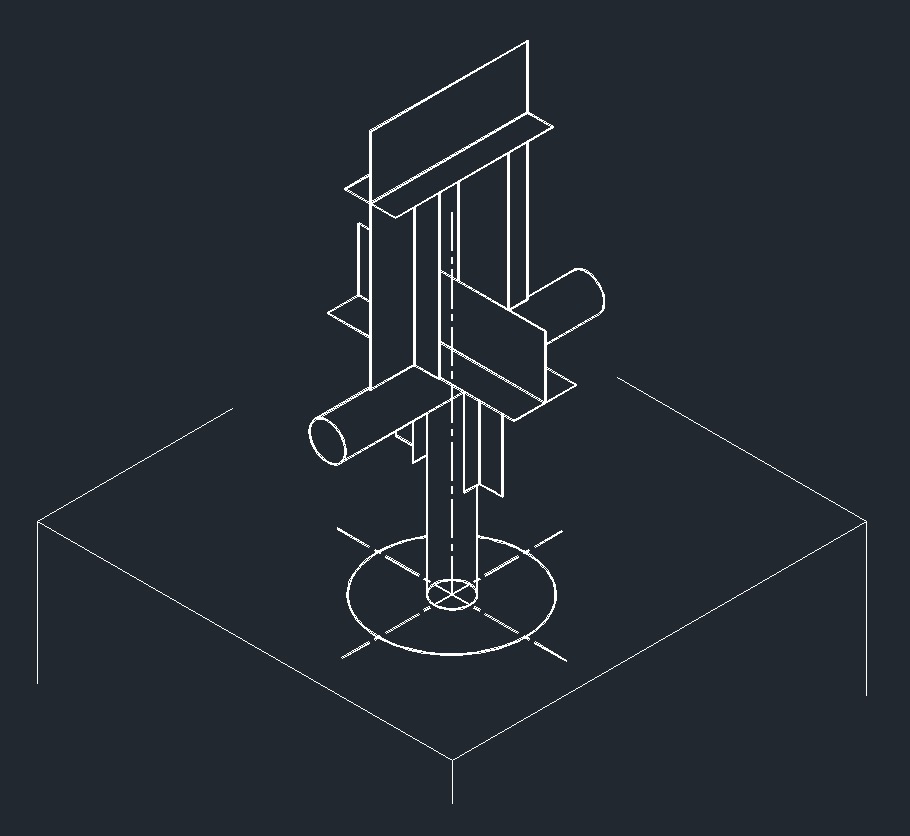 ISO Anchor Left Plane
ISO Anchor Left Plane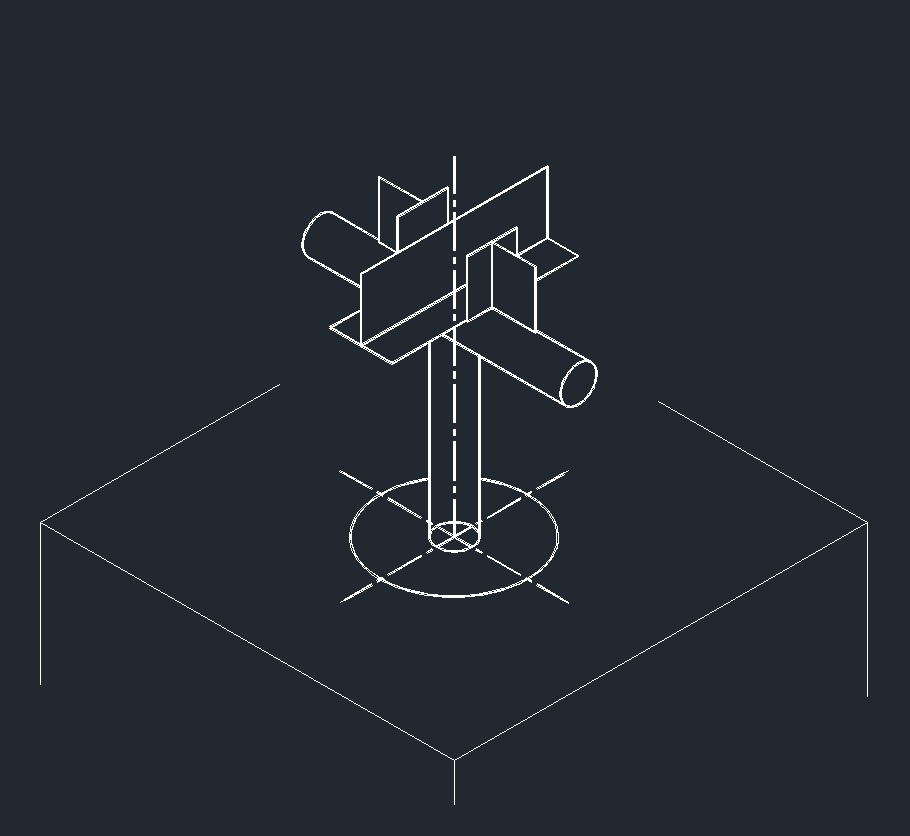 ISO Guide Right Plane
ISO Guide Right Plane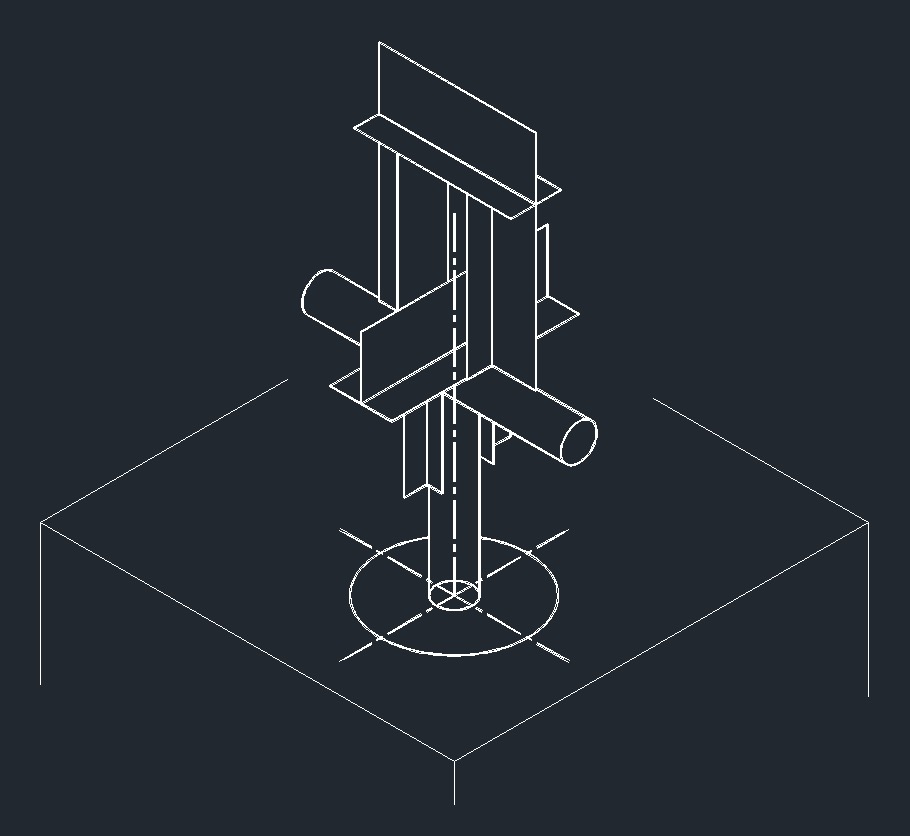 ISO Anchor Right Plane
ISO Anchor Right PlaneBeam Cross Member Guide, Anchor
 ISO Guide Left Plane
ISO Guide Left Plane ISO Anchor Left Plane
ISO Anchor Left Plane ISO Guide Right Plane
ISO Guide Right Plane ISO Anchor Right Plane
ISO Anchor Right Plane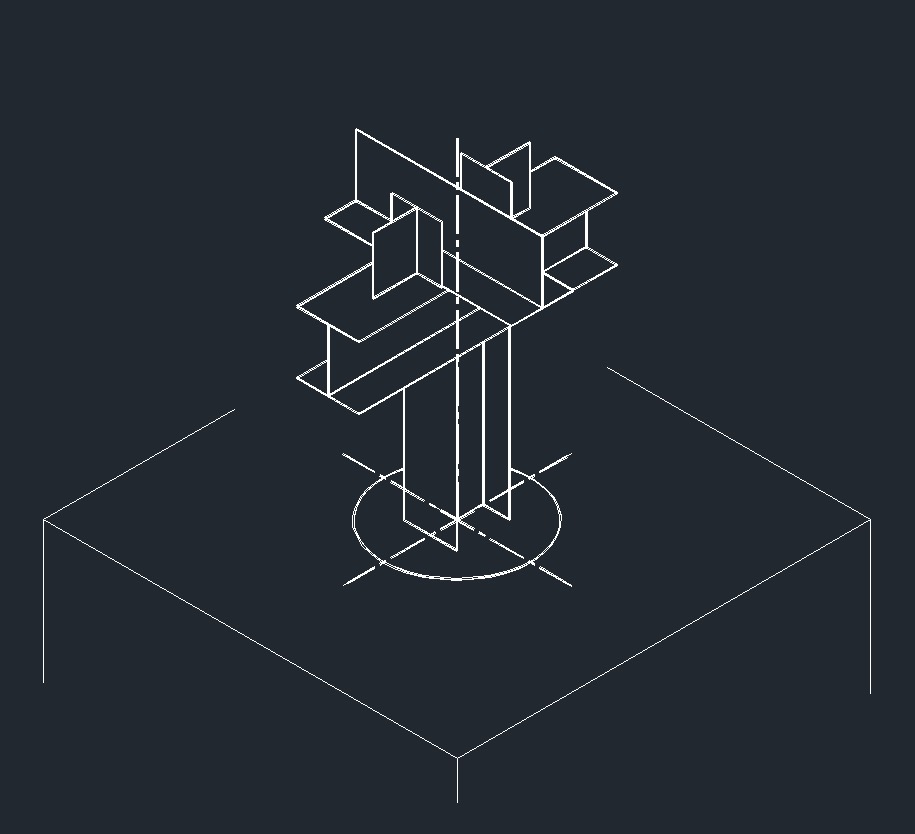 ISO Guide Left Plane
ISO Guide Left Plane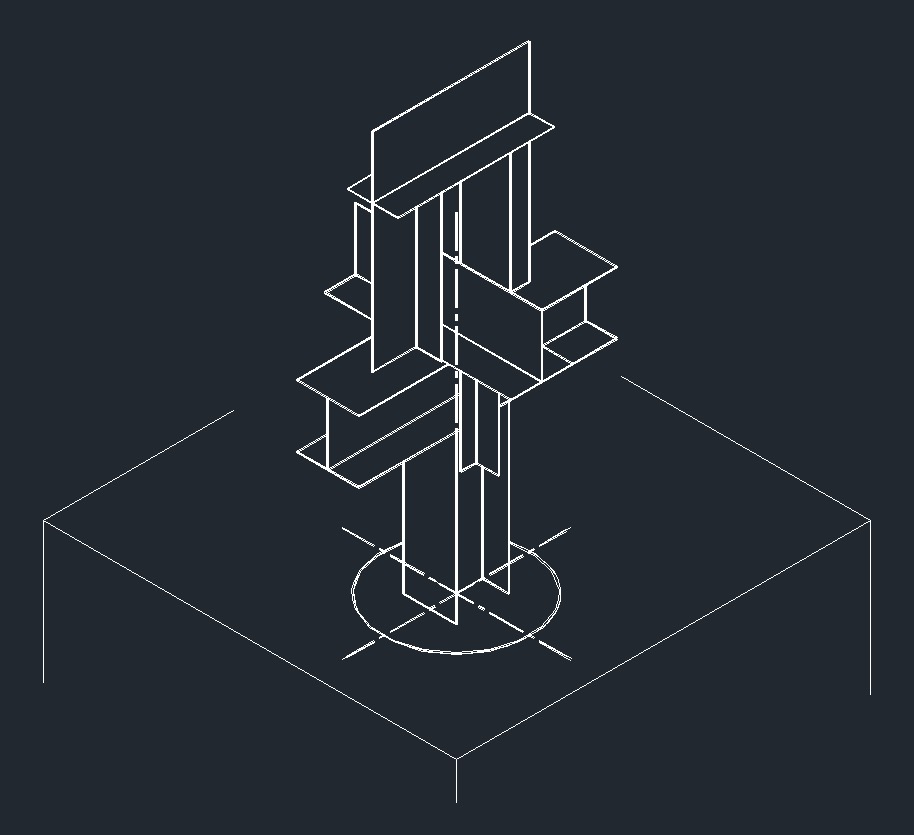 ISO Anchor Left Plane
ISO Anchor Left Plane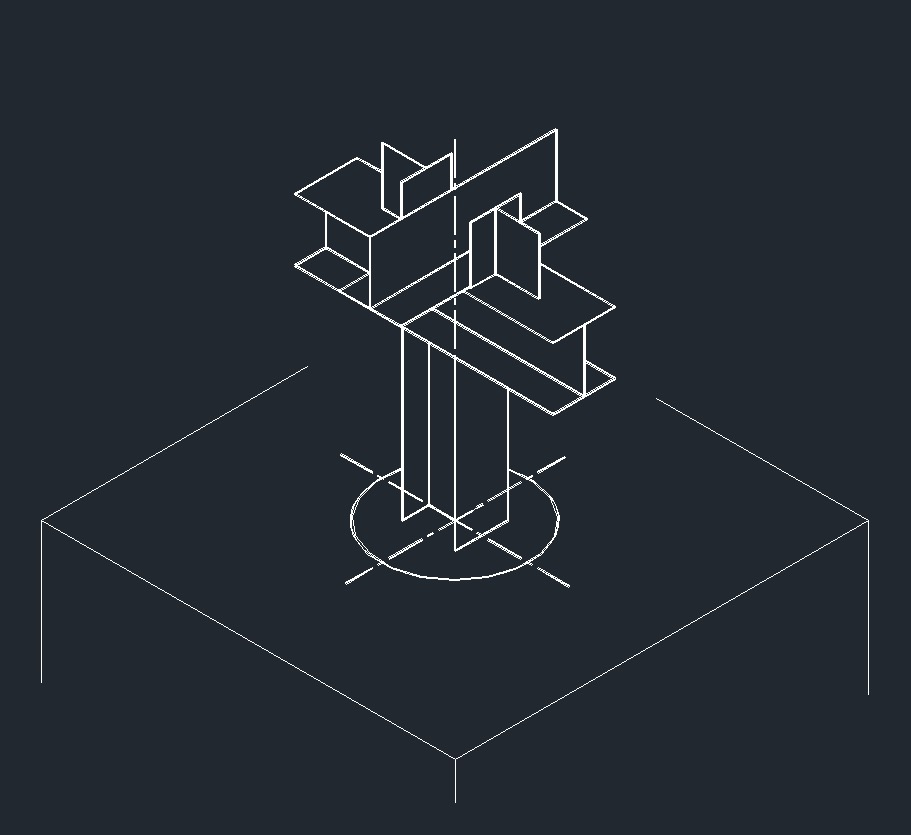 ISO Guide Right Plane
ISO Guide Right Plane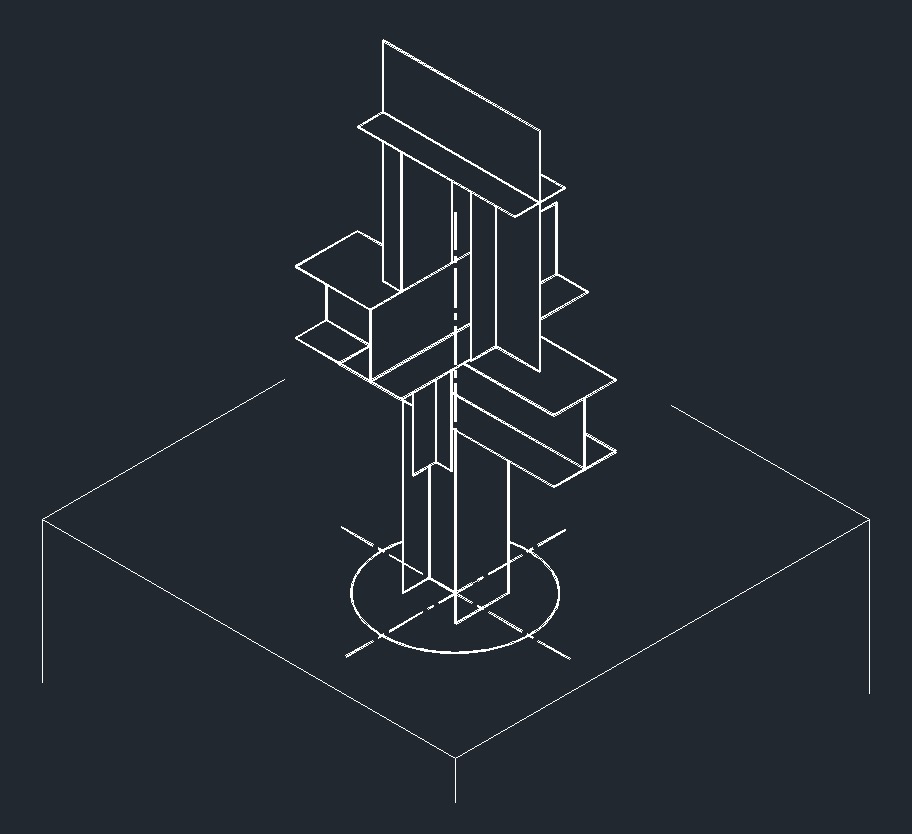 ISO Anchor Right Plane
ISO Anchor Right Plane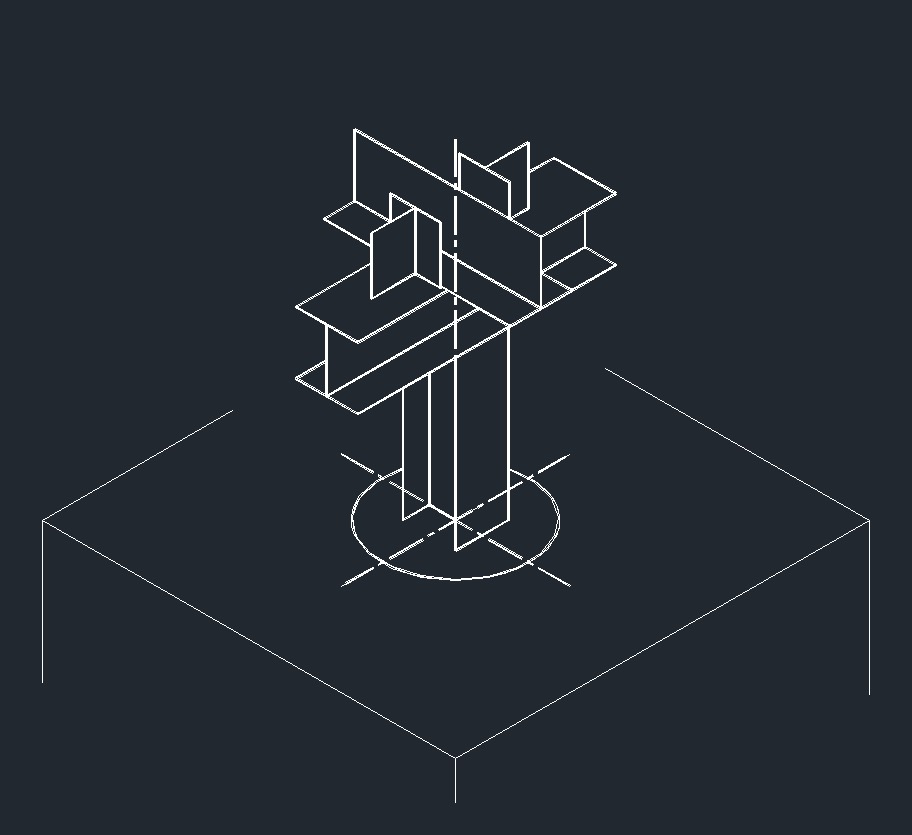 ISO Guide Left Plane
ISO Guide Left Plane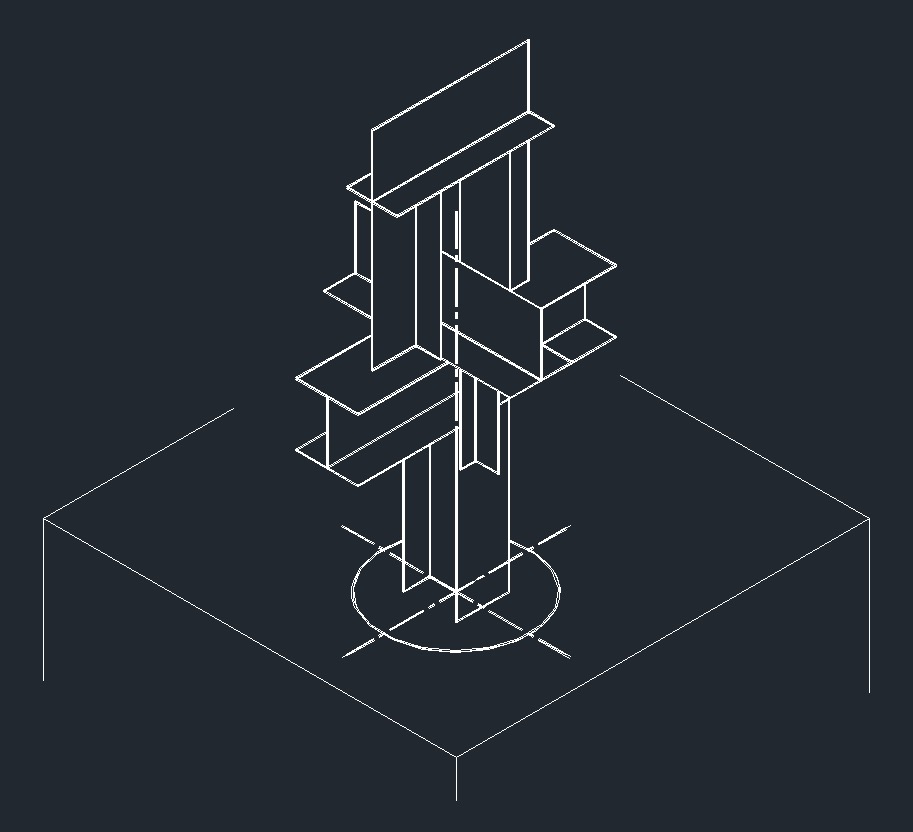 ISO Anchor Left Plane
ISO Anchor Left Plane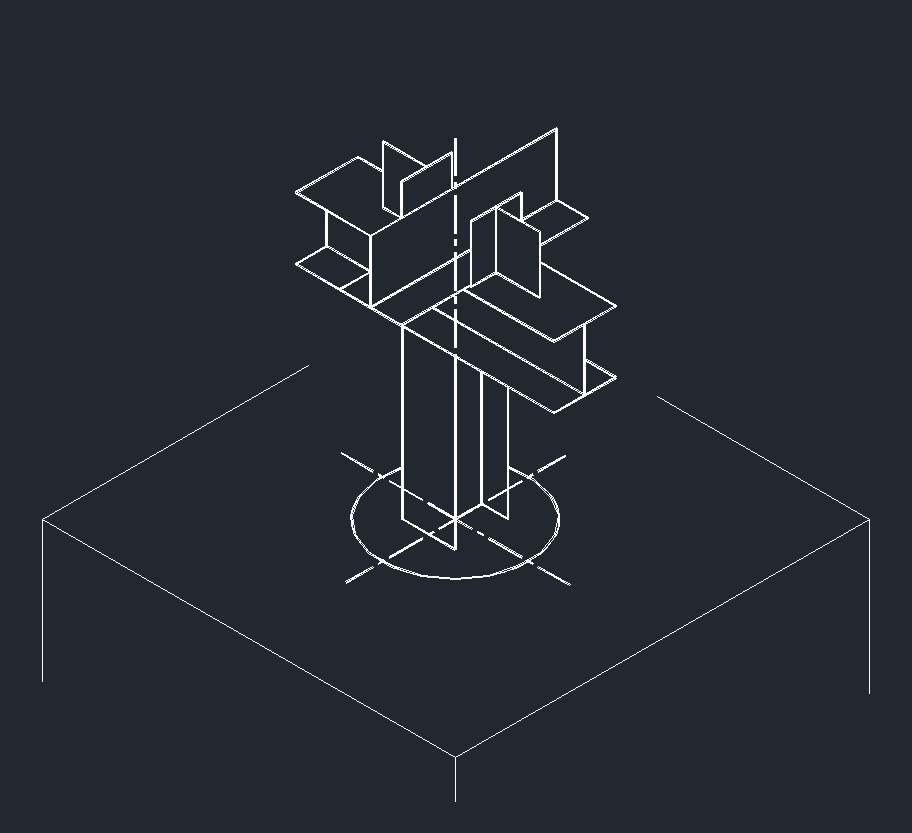 ISO Guide Right Plane
ISO Guide Right Plane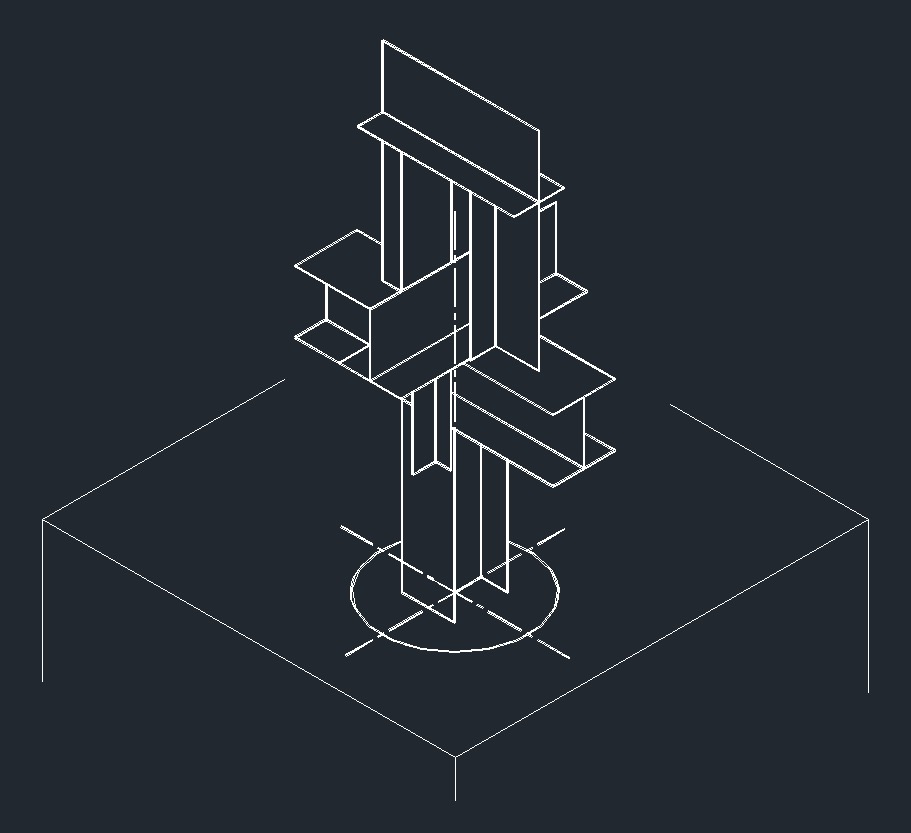 ISO Anchor Right Plane
ISO Anchor Right Plane




