Area Thermal Expansion
Area Thermal Expansion Formula |
||
|
\( \Delta A \;=\; A_f - A_i \) (Area Thermal Expansion) \( A_f \;=\; \Delta A + A_i \) \( A_i \;=\; A_f - \Delta A \) |
||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( \Delta A \) = Area Thermal Expansion | \(in^2\) | \(mm^2\) |
| \( A_f \) = Final Area of the Object | \(in^2\) | \(mm^2\) |
| \( A_i \) = Initial Area of the Object | \(in^2\) | \(mm^2\) |
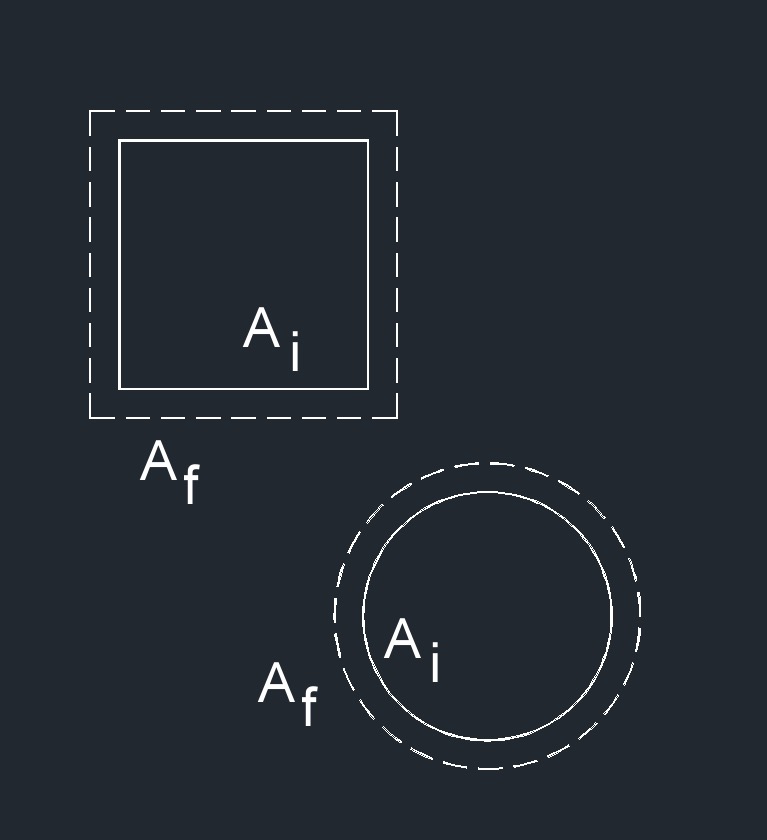 Area thermal expansion, abbreviated as \( \Delta A\), also known as aerial thermal expansion, is the change in size of a two-dimensional surface, such as the surface area of a material, due to temperature changes. It's a concept related to thermal expansion, which describes how materials change in size, volume, or shape when subjected to temperature variations. When a material's temperature increases, its particles gain energy and move more vigorously, causing the material to expand. This expansion can manifest in various ways, including changes in linear dimensions (length, width, height), volume, and surface area.
Area thermal expansion, abbreviated as \( \Delta A\), also known as aerial thermal expansion, is the change in size of a two-dimensional surface, such as the surface area of a material, due to temperature changes. It's a concept related to thermal expansion, which describes how materials change in size, volume, or shape when subjected to temperature variations. When a material's temperature increases, its particles gain energy and move more vigorously, causing the material to expand. This expansion can manifest in various ways, including changes in linear dimensions (length, width, height), volume, and surface area.
Area Thermal Expansion Formula |
||
|
\( \Delta A \;=\; 2 \cdot \overrightarrow{\alpha_l} \cdot A_i \cdot \Delta T \) (Area Thermal Expansion) \( \overrightarrow{\alpha_l} \;=\; \dfrac{ \Delta A }{ 2 \cdot A_i \cdot \Delta T }\) \( A_i \;=\; \dfrac{ \Delta A }{ 2 \cdot \overrightarrow{\alpha_l} \cdot \Delta T }\) \( \Delta T \;=\; \dfrac{ \Delta A }{ 2 \cdot \overrightarrow{\alpha_l} \cdot A_i }\) |
||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( \Delta A \) = Area Thermal Expansion | \(in^2\) | \(mm^2\) |
| \( \overrightarrow{\alpha_l} \) (Greek symbol alpha) = Linear Thermal Expansion Coefficient | \(in \;/\; in\;F\) | \(mm \;/\; mm\;C\) |
| \( A_i \) = Initial Area of the Object | \(in^2\) | \(mm^2\) |
| \( \Delta T \) = Change in Temperature | \(^\circ F\) | \(^\circ C\) |
Understanding and considering area thermal expansion is crucial in various fields, such as materials science, engineering, and manufacturing, where changes in temperature can lead to deformations, stresses, and potential failures if not properly accounted for in design and analysis.

