 Hydrology engineering, also called water resources engineering or hydrological engineering, focuses on the movement, distribution, and management of water resources. It involves studying the hydrologic cycle, how water moves through the atmosphere, land, and oceans, and applying this knowledge to design and manage systems related to water supply, flood control, irrigation, and environmental protection. Hydrologists use various tools, including computer models and simulations, to predict water behavior and design solutions that are both efficient and environmentally sustainable.
Hydrology engineering, also called water resources engineering or hydrological engineering, focuses on the movement, distribution, and management of water resources. It involves studying the hydrologic cycle, how water moves through the atmosphere, land, and oceans, and applying this knowledge to design and manage systems related to water supply, flood control, irrigation, and environmental protection. Hydrologists use various tools, including computer models and simulations, to predict water behavior and design solutions that are both efficient and environmentally sustainable.
Key Areas in Hydrology
Water Supply Systems - Designing systems to provide clean and reliable water to cities, industries, and agriculture.
Flood Control - Managing rivers, lakes, and reservoirs to prevent flooding and mitigate damage to communities and infrastructure.
Drainage Systems - Developing methods to manage stormwater runoff in urban and rural environments.
Irrigation - Designing irrigation systems for agriculture to efficiently use water resources.
Water Quality Management - Ensuring that water bodies remain free of harmful pollutants through proper monitoring and treatment techniques.
Environmental Restoration - Restoring natural water systems that have been impacted by human activities.
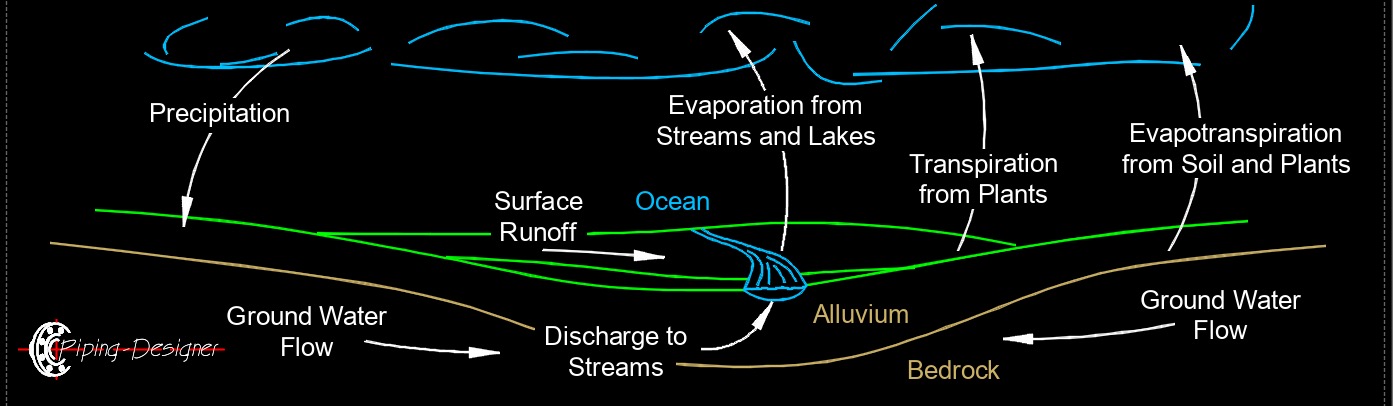
Hydrology Cycles
Hydrological cycle, also called water cycle, is the continuous movement of water on, above, and below the Earth's surface. It is how water moves through different phases and areas, cycling through the atmosphere, land, and oceans. The cycle plays a crucial role in regulating weather patterns, climate, and the availability of freshwater resources.
Water is constantly moving through various phases: liquid (water), vapor (gas), and solid (ice). The cycle is driven by solar energy and gravity, with the sun causing evaporation and the movement of water vapor in the atmosphere, while gravity pulls water back down in the form of precipitation and drives the flow of water across land. It ensures the renewal and distribution of freshwater across the globe, making it essential for ecosystems, agriculture, human consumption, and industrial processes. The hydrological cycle is a self-sustaining system with no beginning or end, constantly circulating water between different reservoirs (oceans, atmosphere, land).
Key Processes of the Hydrological Cycle
Evaporation - Water from oceans, lakes, rivers, and other water bodies heats up and converts into water vapor. This vapor rises into the atmosphere.
Transpiration - Plants absorb water through their roots and release it as water vapor through tiny pores in their leaves. This process contributes to the overall moisture in the atmosphere.
Condensation - As water vapor rises, it cools and condenses into tiny droplets, forming clouds. These droplets combine to create larger water particles, which can result in rain or other forms of precipitation.
Precipitation - When clouds accumulate enough moisture, water falls back to the Earth's surface as rain, snow, sleet, or hail, depending on the temperature and atmospheric conditions.
Infiltration - Some of the water from precipitation seeps into the ground, replenishing groundwater supplies and aquifers. This infiltrated water can also be absorbed by plant roots.
Surface Runoff - Water that does not infiltrate into the ground flows over the surface as runoff. This water moves toward rivers, lakes, and oceans, contributing to the return of water to larger bodies of water.
Subsurface Flow (Groundwater Flow) - Water that has infiltrated into the ground can move through soil and rocks as groundwater. Some of this water eventually flows back into rivers, lakes, or oceans, completing the cycle.
Sublimation (less common) - Sublimation is the direct conversion of ice or snow into water vapor without passing through a liquid phase. This typically occurs in cold, dry regions like glaciers and snowpacks.

 Hydrology engineering, also called water resources engineering or hydrological engineering, focuses on the movement, distribution, and management of water resources. It involves studying the hydrologic cycle, how water moves through the atmosphere, land, and oceans, and applying this knowledge to design and manage systems related to water supply, flood control, irrigation, and environmental protection. Hydrologists use various tools, including computer models and simulations, to predict water behavior and design solutions that are both efficient and environmentally sustainable.
Hydrology engineering, also called water resources engineering or hydrological engineering, focuses on the movement, distribution, and management of water resources. It involves studying the hydrologic cycle, how water moves through the atmosphere, land, and oceans, and applying this knowledge to design and manage systems related to water supply, flood control, irrigation, and environmental protection. Hydrologists use various tools, including computer models and simulations, to predict water behavior and design solutions that are both efficient and environmentally sustainable.
