Electrical Engineering
Science Branches |
| Science |
| Applied Science |
| Engineering |
| Electrical Engineering |
|
Electrical engineering is a branch of engineering that deals with the study, design, development, and implementation of electrical and electronic systems, including power generation and transmission, communication systems, control systems, and electronic circuits. Electrical engineers work in a variety of industries, including power generation and distribution, telecommunications, electronics, and manufacturing. They may work in research and development, product design, systems analysis, or project management, depending on their area of specialization.
- See Articles - List of Tags, List of Categories, List of Articles, List of Glossaries, Nomenclature and Symbols, (See Electrical Glossary), (See Instrumentation and Controls Glossary)
Electric Wire Materials
Energy Types
Renewable Energy - Renewable energy sources are naturally replenished. Day after day, the sun shines, plants grow, wind blows, and rivers flow.
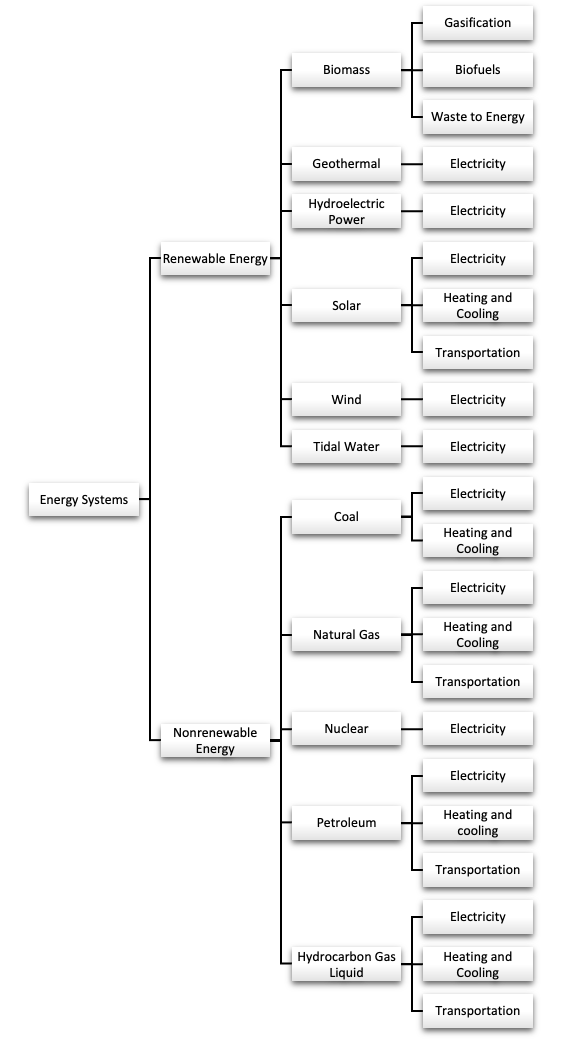 Biomass - The organic material that comes from plants and animals, and it is a renewable source of energy. Biomass can be used directly for heating or converted into biofuels for transportation and electricity generation.
Biomass - The organic material that comes from plants and animals, and it is a renewable source of energy. Biomass can be used directly for heating or converted into biofuels for transportation and electricity generation.- Geothermal - A form of renewable energy that is generated by harnessing the natural heat from within the Earth. This heat comes from the decay of radioactive materials in the Earth's core and the residual heat from the planet's formation.
- Hydroelectric - Hydropower, also known as hydroelectric power, is a form of renewable energy that uses the movement of water to generate electricity. It typically involves harnessing the kinetic energy of flowing or falling water, such as in rivers or from man-made reservoirs, to spin turbines connected to generators.
- Solar - The energy that comes from the sun and is harnessed using various technologies to generate electricity, heat, or to support other processes. It is a renewable and sustainable source of energy, meaning it can be replenished naturally and doesn't deplete resources.
- Tidal Water - A form of renewable energy generated by harnessing the movement of tides. Tides are the rise and fall of sea levels caused by the gravitational forces exerted by the moon and the sun, along with the rotation of the Earth. Tidal energy is considered a predictable and reliable source of power, unlike other renewable sources like wind and solar, which can be more variable.
- Wind - A form of renewable energy that harnesses the power of the wind to generate electricity. It is produced using wind turbines, which are large structures with blades that rotate when the wind blows. The movement of the blades turns a generator inside the turbine, converting the kinetic energy of the wind into electrical energy.
Nonrenewable Energy - These energy sources supplies are limited to the amounts that we can mine or extract from the earth. Coal, natural gas, and petroleum formed over thousands of years from the buried remains of ancient sea plants and animals that lived millions of years ago, which is why we also call those energy sources fossil fuels.
- Coal - The process of generating electricity by burning coal, a fossil fuel that has been used for centuries as a primary energy source. Coal energy has played a crucial role in powering industrialization and modern economies, but its environmental impact has led to a shift toward cleaner, renewable energy sources like wind, solar, and hydropower.
- Hydrocarbon Gas Liquid - Hydrocarbon gas liquids (HGL) are hydrocarbons that occur as gases at atmospheric pressure and as liquids under higher pressures. HGLs can also be liquefied by cooling. The specific pressures and temperatures at which the gases liquefy vary by type of HGL. HGLs may be described as being light or heavy according to the number of carbon atoms and hydrogen atoms in an HGL molecule.
- Natural Gas - A source of energy for generating electricity, heating, and powering various industrial processes. Natural gas is a fossil fuel composed primarily of methane (\(CH_4\)) and is found deep beneath the Earth's surface, often along with oil deposits. Natural gas plays a significant role in the global energy mix, particularly as a bridge fuel with sustainable energy sources.
- Nuclear - The energy released during nuclear reactions, particularly in the process of nuclear fission or fusion. Nuclear energy continues to be a subject of debate, balancing its potential benefits against its risks and challenges.
- Petroleum - Energy deriisved from petroleum, a fossil fuel that is formed from the remains of ancient marine organisms buried under layers of sediment and subjected to heat and pressure over millions of years. Petroleum, also known as crude oil, is a complex mixture of hydrocarbons that can be refined into various products such as gasoline, diesel, jet fuel, heating oil, and other petrochemicals. Petroleum energy has been a cornerstone of modern industry and transportation, but its environmental impact has led to increasing interest in renewable energy sources.

Tags: Electrical Instrumentation and Controls Engineering Network Theorems

