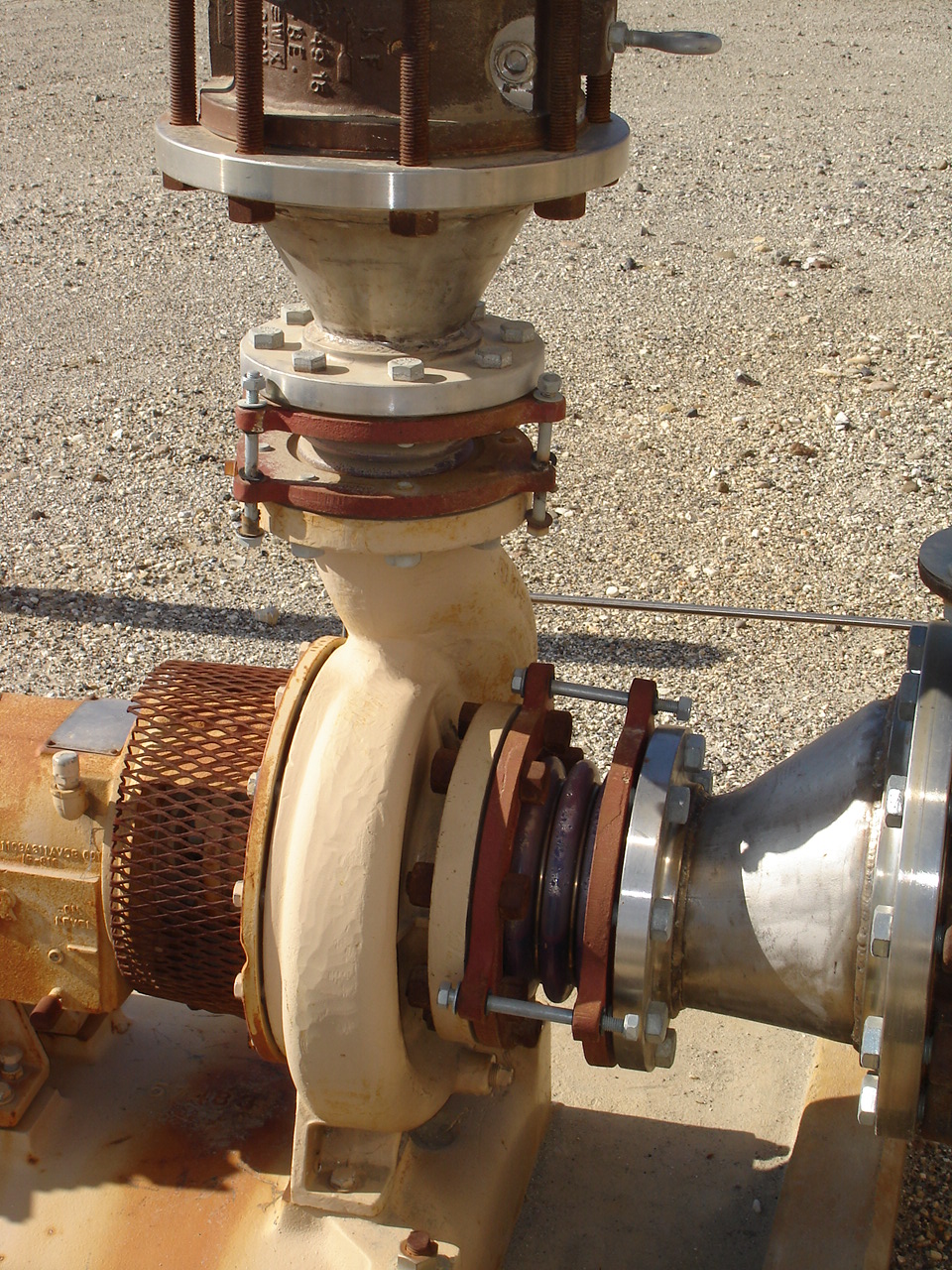
Common Materials used for Expansion Joints
Expansion joints are used in various construction and engineering applications to allow for the expansion and contraction of materials due to temperature changes, vibrations, or other factors. The choice of material for expansion joints depends on the specific application, environmental conditions, and the intended purpose of the joint.
Rubber - Rubber is a popular choice for expansion joints, especially in buildings and bridges. Neoprene rubber and EPDM (Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer) rubber are commonly used due to their flexibility, durability, and resistance to various environmental factors. Rubber expansion joints are often used in applications where movement is relatively limited.
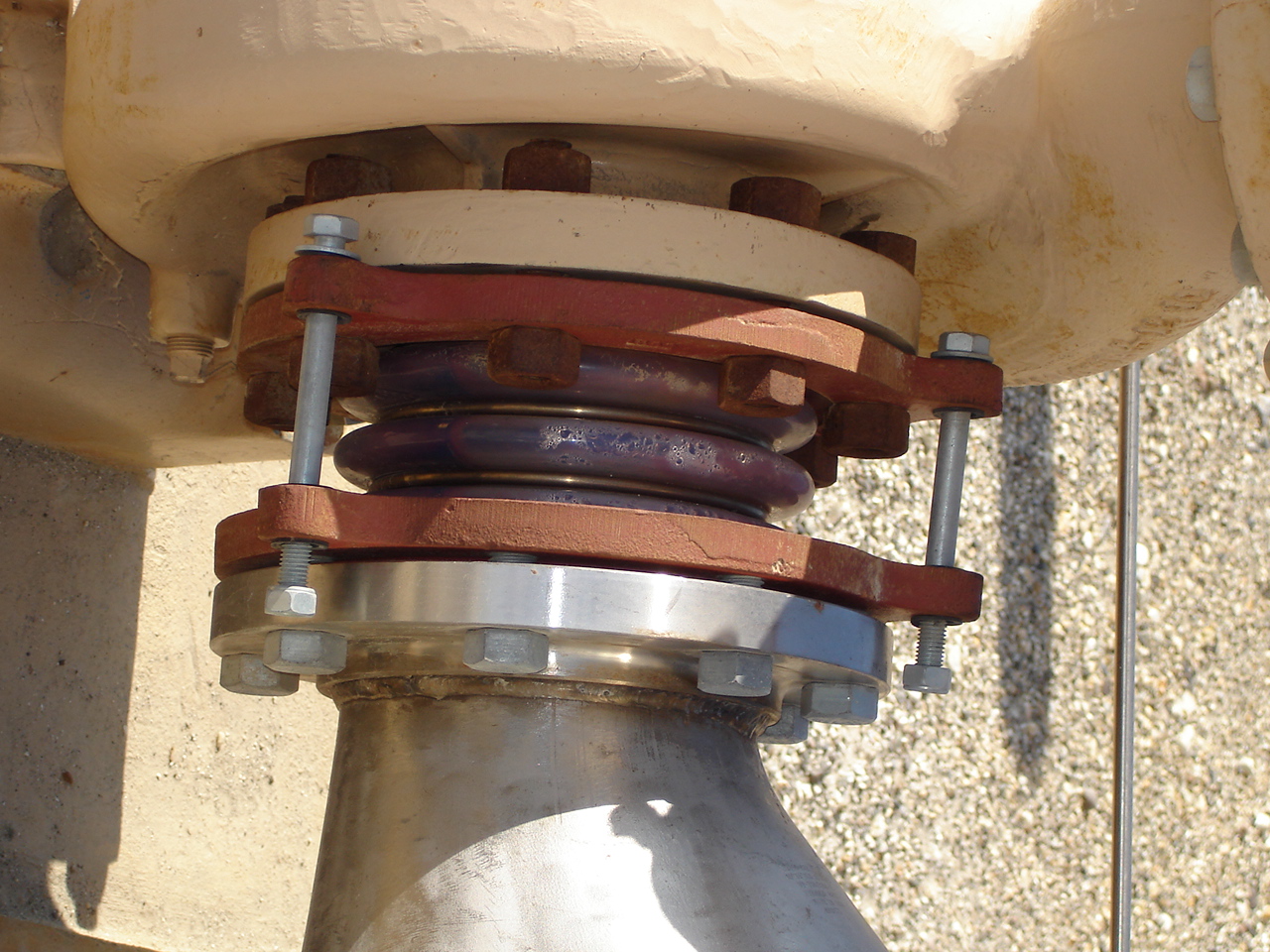
Metal - Metal expansion joints are used in applications that involve high temperatures, high pressures, or where large movements are expected. Materials such as stainless steel, carbon steel, and other alloys are used to make metal expansion joints. They are often used in industrial piping systems, power plants, and other heavy duty applications.
Fabric - Fabric expansion joints are used in applications that require flexibility and resistance to vibration. They are typically made from various fabric materials, such as fiberglass, Teflon coated fiberglass, or other high temperature resistant materials. Fabric expansion joints are commonly used in exhaust systems, HVAC systems, and industrial ducting.
Composite - Composite expansion joints combine multiple materials to achieve specific properties. For example, they may consist of layers of rubber and fabric or rubber and metal to provide flexibility and durability. Composite expansion joints are used in a wide range of applications, including bridges, pipelines, and industrial machinery.
Concrete - In some construction applications, especially for bridges and roadways, concrete expansion joints are used. These joints are typically made of preformed or poured-in place concrete and are designed to accommodate the expansion and contraction of concrete slabs to prevent cracking and damage.
Polymer - Polymer-based expansion joints, such as polyurethane or silicone, are used in various applications, including flooring systems, sidewalks, and parking structures. These materials offer flexibility and durability, making them suitable for accommodating movement in these types of structures.
Fiber Reinforced Polymer (FRP) - FRP materials, such as fiberglass or carbon fiber composites, are used in some structural and industrial applications. They offer lightweight and high strength properties and can be used in expansion joints in bridges and buildings.
Bituminous Materials - Bituminous expansion joint materials are made from asphalt based compounds and are often used in road construction for expansion joints in concrete or asphalt pavements.