Circle
- Article Link - Geometric Properties of Structural Shapes
area of a Circle formulas |
||
|
\( A \;=\; \pi \cdot r^2 \) (Radius) \( A \;=\; \dfrac{ \pi \cdot d^2 }{ 4 }\) (Diameter) \( A \;=\; \dfrac{ C^2 }{ 4 \cdot \pi }\) (Circumference) |
||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( A \) = area | \( in^2 \) | \( mm^2 \) |
| \( C \) = circumference | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( d \) = diameter | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( \pi \) = Pi | \(3.141 592 653 ...\) | \(3.141 592 653 ...\) |
| \( r \) = radius | \(\large{ in }\) | \( mm \) |
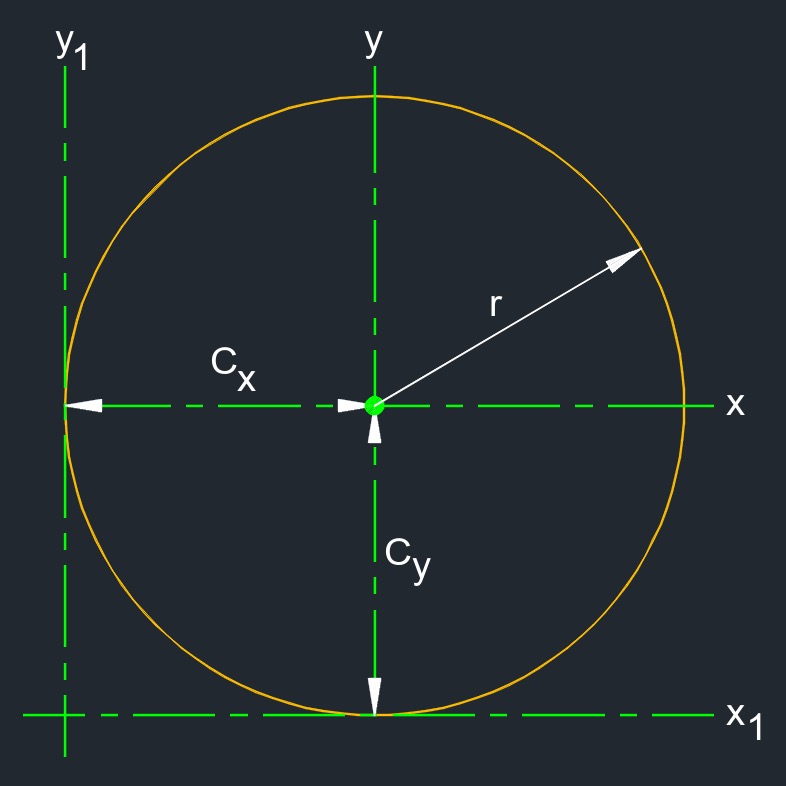
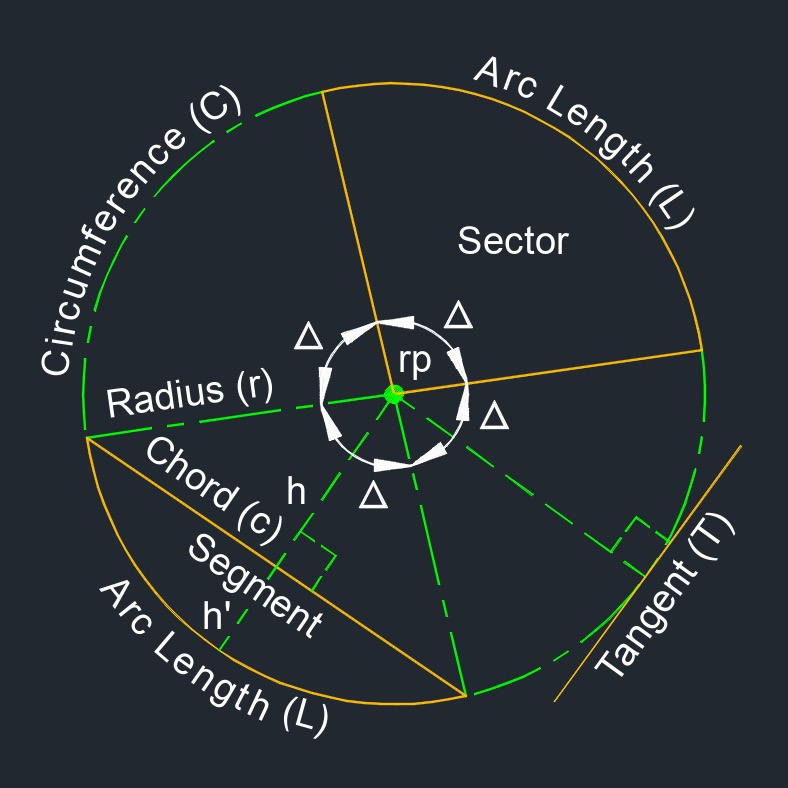
- Circle - All points are at a fixed equal distance from a radius point (rp).
- Angle (\(\Delta\)) - Two rays sharing a common point.
- Center (cp) - Having all points on the line circumference are at equal distance from the center point.
- Chord (c) - Also called long chord (LC), is between any two points on a circular curve.
- Circumference (C) - The outside of a circle or a complete circular arc.
Circumference of a Circle formulas |
||
|
\( C \;=\; 2 \cdot \pi \cdot r \) \( C \;=\; \pi \cdot d \) \( C \;=\; 2 \cdot \sqrt{ \pi \cdot A } \) \( C \;=\; \dfrac{ 2 \cdot A }{ r }\) |
||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( C \) = circumference | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( A \) = area | \( in^2 \) | \( mm^2 \) |
| \( d \) = diameter | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( \pi \) = Pi | \(3.141 592 653 ...\) | \(3.141 592 653 ...\) |
| \( r \) = radius | \( in \) | \( mm \) |

- Diameter (d) - Is any straight line segment that passes through the center of the circle and whose endpoints are on the circle. The diameters are the longest chords of the circle. In the process industry, the diameter is typically used to describe the size pipe that the process is flowing through. Unless explictily specified, the diameter is assumed to mean the nominal pipe size (NPS). The inside diameter of a pipe is the longest distance between the two inside walls of the pipe. The outside diameter is the distance between the two outside walls. To find the thickness of the pipe, subtract the outside diameter from the inside diameter and divide by two. When sizing flow meters or impact tees, a certain straight run maybe required. This is typically specified in terms of diameters. For example a 10" orifice meter with a 10 diameter upstream requirement will require 100" of unobstructed straight run upstream of the orifice plate.
Diameter of a Circle formulas |
||
|
\( d \;=\; 2 \cdot r \) \( d \;=\; \dfrac{ C }{ \pi }\) \( d \;=\; \sqrt{ \dfrac{ 4 \cdot A }{ \pi } }\) |
||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( d \) = diameter | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( A \) = area | \( in^2 \) | \( mm^2 \) |
| \( C \) = circumference | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( \pi \) = Pi | \(3.141 592 653 ...\) | \(3.141 592 653 ...\) |
| \( r \) = radius | \( in \) | \( mm \) |

- Height (h) - Length of radius from radius center to midpoint of chord.
- Height (h') - Length of radius from midpoint of chord to point on circular curve.
- Length (L) - Total length of any circular curve measured along the arc.
- Major Arc - The longest of two arcs of a circle or ellipse.
- Minor Arc - The shorter of two arcs of a circle or ellipse.
- Radius (r) - Half the diameter of a circle. A line segment between the center point and a point on a circle or sphere.
- Radius Point (rp) - Radius center point of circular curve.
- Sector is a fraction of the area of a circle with a radius on each side and an arc.
Radius of a Circle formulas |
||
|
\( r \;=\; \dfrac{ d }{ 2 }\) \( r \;=\; \dfrac{ C }{ 2 \cdot \pi }\) \( r \;=\; \sqrt{ \dfrac{ A }{ \pi } }\) \( r \;=\; \dfrac{ 2 \cdot A }{ C }\) \( r \;=\; \sqrt{ \dfrac{ c^2 }{ 4 } + h^2 } \) \( r \;=\; \dfrac{ L }{ \Delta }\) \( r \;=\; h + h' \) |
||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( r \) = radius | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( \Delta \) = angle | \( deg \) | \( rad \) |
| \( A \) = area | \( in^2 \) | \( mm^2 \) |
| \( c \) = chord | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( C \) = circumference | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( d \) = diameter | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( h \) = length of radius from radius center to midpoint of chord. | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( h' \) = length of radius from midpoint of chord to point on circular curve. | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( L \) = length of any circular curve measured along the arc. | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( \pi \) = Pi | \(3.141 592 653 ...\) | \(3.141 592 653 ...\) |
| \( r \) = radius | \( in \) | \( mm \) |

- Segment is an interior part of a circle bound by a chord and an arc.
- Tangent (T) - A line that touches a curve at just one point such that it is perpendicular to a radius line of the curve.

