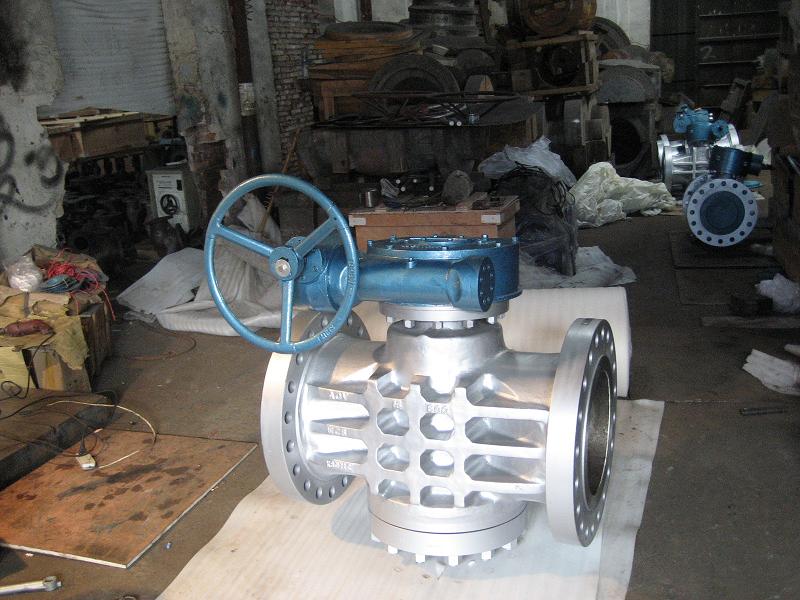
 Duplex Plug Valve with a handwheel
Duplex Plug Valve with a handwheel
A plug valve is a quarter turn valve that has a conical or cylindrical plug that is rotated within the valve body to stop flow when needed. Plug valves function similar to a ball valve where the plug has an opening in the plug that allows fluid to flow through the valve when it is open.
Plug valves can be used as a double block and bleed valve by installing a bleeder on the body of the valve. When the valve is closed, the bleeder dcan be opened to ensure there is zero flow through the valve.
Plug Valve Design Classification
Eccentric Plug Valve - These valves are used for numerous flow control and isolation applications that basically includes clean and dirty water, sewage, sludge and slurries, and etc. The plug has no contact with its seat until it turns within a few degrees of the shutoff position. As the plug contacts into the seat, the seating surfaces dynamically align to achieve shutoff.
Expanding Plug Valve - These valves uses multiple components tand a complex rotation motion that helps in avoiding wear or abrasions to the seals. They are a good fit for preventing product contamination in applications that do not require double isolation. In an expanding plug valve, the
slips are retracted from the wall prior to completing the quarter turn, so you have no friction. Less
friction means less wear, and maintenance over
time.
Fire-safe Plug Valve - Fire safety plug valves use a narrowb and primary sealing ring made of a flexible, elastic material (such as Teflon) in the ring between the plug and the body cavity to prevent leakage. A fire safe soft seal valve also has a secondary metal to metal backup seal. This ensures a positive closing capability if the soft seal is damaged by fire. The maximum temperature limit of the valve is limited by the soft-seal material.
Lift Plug Valve - This valve provides a mechanical lifting arrangement to disengage the tapered plug from the seating surface to permit easy rotation. The lifting can be achieved by an external lever.
Lubricated Plug Valve - The plug is designed with grooves, which retain a lubricant (base oil and
viscosity improver) to seal and lubricate the valve and prevent stricking and provide a
hydraulic jacking force to lift the plug within the body. This reduces the force required for rotary operation and assists in sealing the surface of the valve stem. The lubricant is injected into the valve under pressure to reduce friction and to provide a seal between the valve’s seating surfaces. Lubricated plug valves are high maintenance as they need to be lubricated regularly.
Non-lubricated Plug Valve - Non-lubricated plug valves are usually used for lower
pressure lines, and their valve seats tend to deteriorate quicker from the wear and tear of dust, dirt and other debris, compared to those on the lubricated plug valves. Non-lubricated plug valves are often chosen for use over lubricated plug valves because they require minimal maintenance.
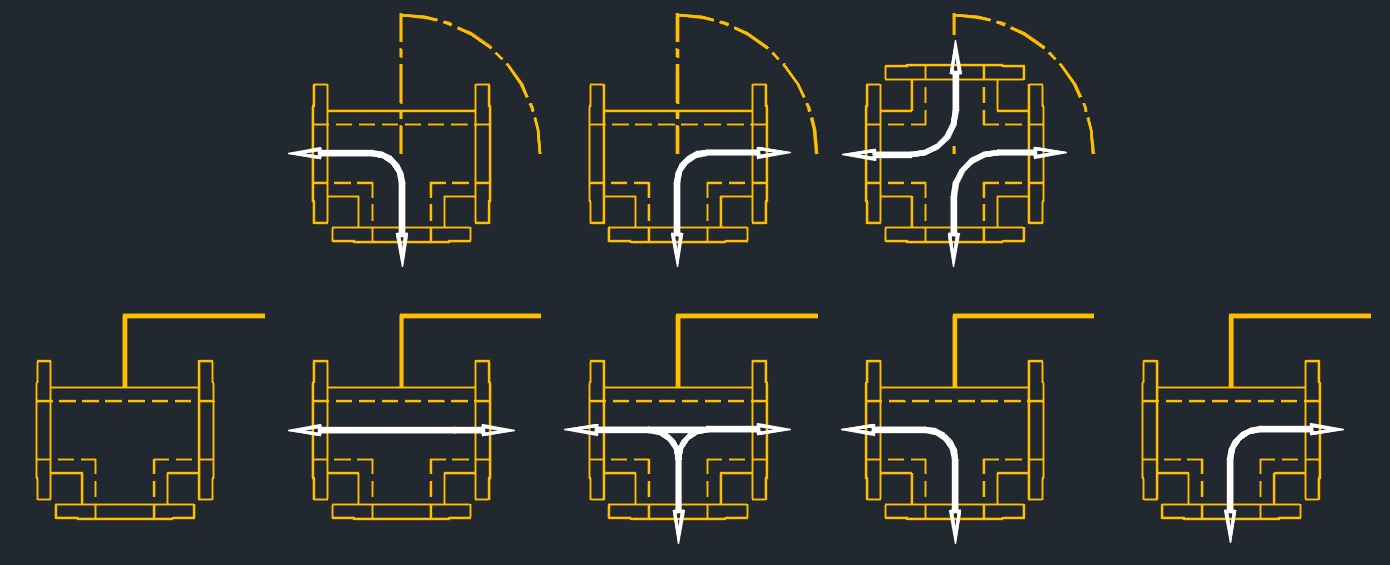 Multi-port Plug Valve
Multi-port Plug Valve - One 3-way or 4-way multiport valve may be used in place of two, three or four straightway valves, and in most cases will also eliminate other
fittings such as tees and elbows. Multi-port valves have ports arranged so that when the plug is turned from one position to another, the channels previously in connection will be entirely closed before new channels begin to open. This will preventing mixture of fluids or loss of pressure.
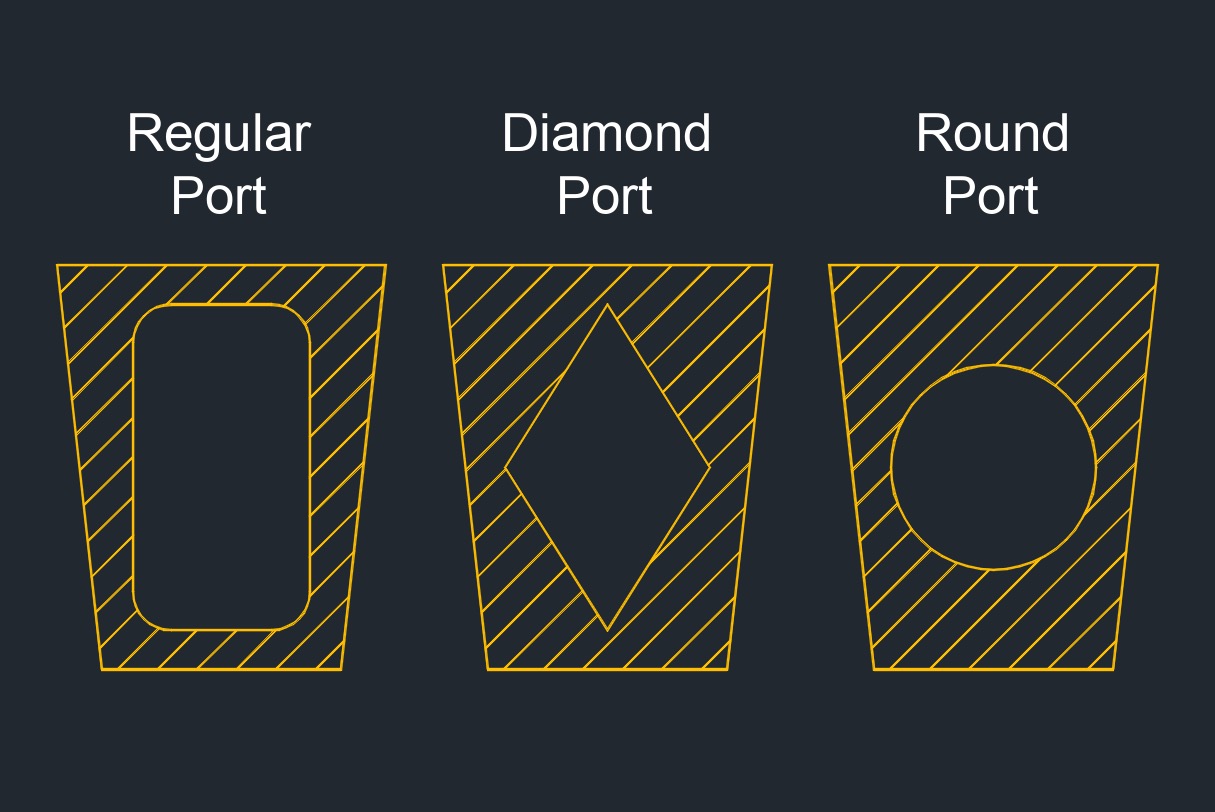 Plug Valve Port Styles
Plug Valve Port Styles
Rectangular Port - The most common port shape for plug valve. The rectangular port represents at least 70% of the cross-sectional area of the corresponding pipe.
Diamond Port - Has a diamond-shaped port through the plug. The port is venturi restricted flow type. The design is well suited for throttling service.
Round Port - Has a round port through the plug. If the
diameter of the port is the same as or larger than the inside diameter of the pipe, this is a full port, also called full bore. If the diameter of the port is smaller than the inside diameter of the
pipe, this is a standard round port.
Plug Valve Pattern Styles
Regular Pattern Plug Valve - A term usually applied to plug valves. The regular port is normally about 40% of the line pipe area. It corresponds to a venture or reduced bore valve of like
nominal pipe size.
Short Pattern Plug Valve - A valve whose face-to-face dimension is less than the API-6D standard.
Venturi Pattern Plug Valve - A reduced bore valve. A valve having a bore smaller in diameter than the inlet or outlet. For example, an 8"x 6" x 8" ball valve has 8" inlet and outlet connections while the ball and seats are 6". The flow through a venture valve will be reduced because of the smaller port. Venturi valves can often be economically substituted for plug valves.
Plug Valve Advantages and Disadvantages
|
|---|
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|
- Widely used, especially in low pressure, small diameter and medium temperature.
- A one piece, top entry body valve design, except the top flange.
- A good choice for a lot of corrosive, abrasive and toxic fluid as well as continuously operated device.
- Good sealing performance.
- Coated bushing provides the characteristics of face sealing.
- Can be serviced in place.
- The fluid resistance is small.
- No vibration and low noise.
- Plug valve come in various body designs, three-way, four-way, five-way and six-way valve; double valve group or valves group; all kinds of jacket requirements, etc..
- This valve is suitable for many harsh media such as easy crystallization, viscosity, containing catalyst particles and corrosion fluid deposition.
- Plug valve is economical due to its high reliability, low total cost and other incomparable advantages.
|
- Requires greater force to actuate, due to high friction.
- The design of face sealing improves the requirements for driving torque.
- The plug valve investment is higher than the ball valve.
- Larger valves require the use of actuators.
|

 Duplex Plug Valve with a handwheel
Duplex Plug Valve with a handwheel Multi-port Plug Valve - One 3-way or 4-way multiport valve may be used in place of two, three or four straightway valves, and in most cases will also eliminate other fittings such as tees and elbows. Multi-port valves have ports arranged so that when the plug is turned from one position to another, the channels previously in connection will be entirely closed before new channels begin to open. This will preventing mixture of fluids or loss of pressure.
Multi-port Plug Valve - One 3-way or 4-way multiport valve may be used in place of two, three or four straightway valves, and in most cases will also eliminate other fittings such as tees and elbows. Multi-port valves have ports arranged so that when the plug is turned from one position to another, the channels previously in connection will be entirely closed before new channels begin to open. This will preventing mixture of fluids or loss of pressure. Plug Valve Port Styles
Plug Valve Port Styles





