Capacitance
Capacitance Formula |
||
|
\( C \;=\; \dfrac{ Q }{ V }\) (Capacitance) \( Q \;=\; C \cdot V \) \( V \;=\; \dfrac{Q }{ C }\) |
||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( C \) = Capacitance | \(F\) | \(F\) |
| \( Q \) = Electric Charge that is Stored on the Capacitor | \(C\) | \(C\) |
| \( V \) = Potential Difference (the Voltage Between the Capacitor's Plates) | \(V\) | \(V\) |
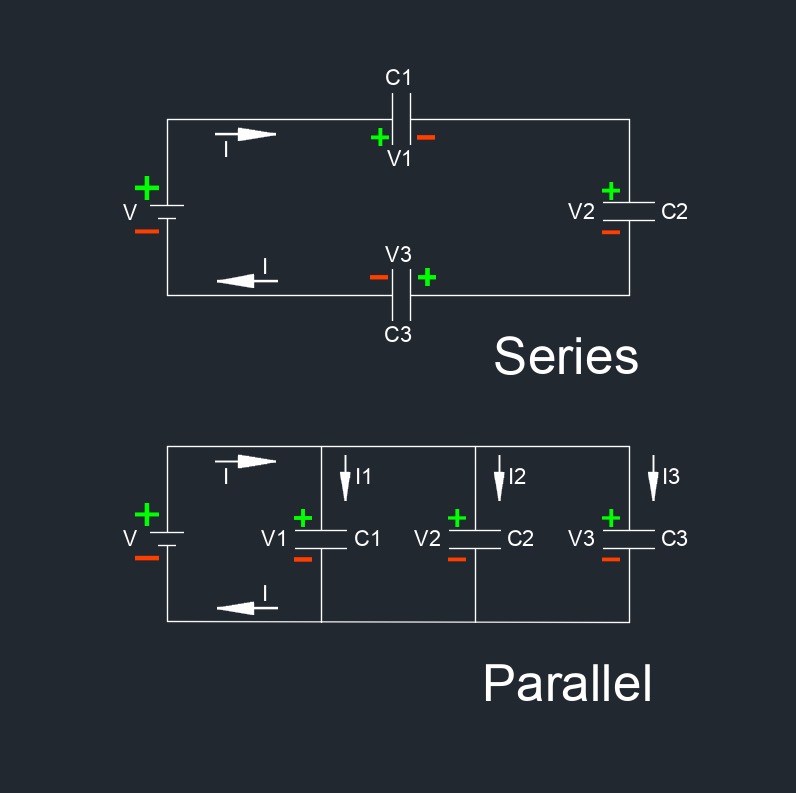
Capacitance, abbreviated as \(C\) or \(CAP\), is the ability of a system to store electrical charge. The capacitance of a system depends on its physical characteristics and the arrangement of its components. In other terms, capacitance quantifies how much charge a capacitor can store per unit of voltage. A capacitor is a two terminal electronic component that consists of two conductive plates separated by an insulating material called a dielectric. The larger the surface area of the plates and the smaller the separation between them, the higher the capacitance.
This equation illustrates that the current flowing into or out of a capacitor is proportional to the rate of change of voltage across the capacitor. As a result, capacitors are often used in electronic circuits for various purposes, such as energy storage, smoothing voltage fluctuations, and filtering signals. Capacitance plays a role in the behavior of many electrical systems and is a key parameter in the design and analysis of electronic circuits.

