Heat Transfer by Radiation
Heat Transfer by Radiation Formula |
||
| \( Q_r \;=\; \sigma \cdot A \cdot ( T^4 - T_e^4 ) \) | ||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( Q_r \) = Heat Radiation | \(Btu\;/\;hr\) | \( W \) |
| \( \sigma \) (Greek symbol sigma) = Stefan-Boltzmann Constant | \(Btu\;/\;hr-ft^2-R^4\) | \(W\;/\;m^2-K^4\) |
| \( A \) = Radiation Area | \( in^3 \) | \( mm^3 \) |
| \( T \) = Emitting Object Temperature | \(^\circ R \) | \(^\circ K \) |
| \( T_e \) = Environmental Temperature | \(^\circ R \) | \(^\circ K \) |
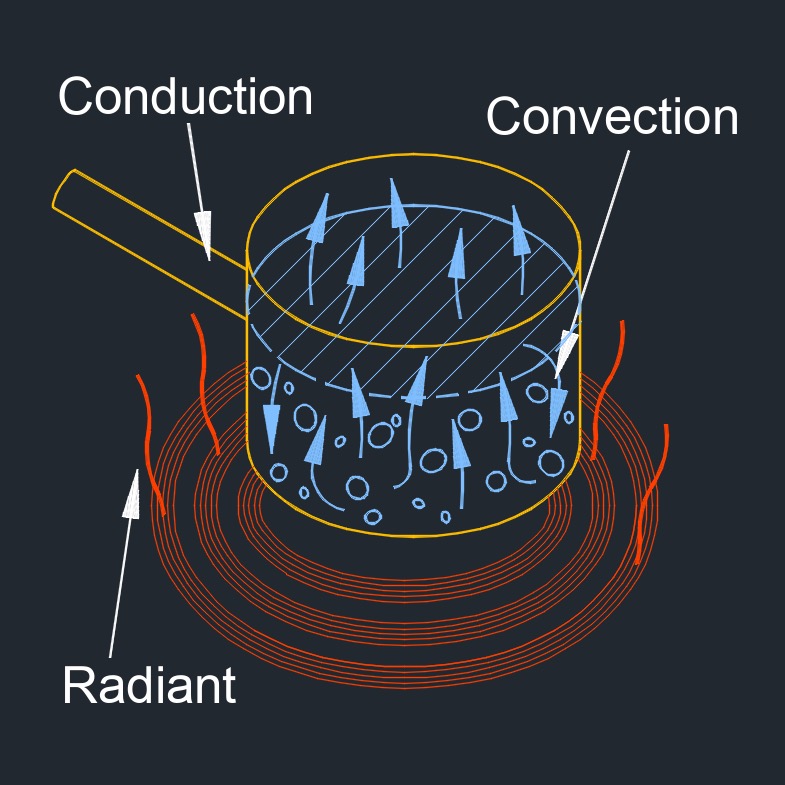 Heat transfer by radiation, abbreviated as \(Q_r\) or \(\phi\) (Greek symbol phi), also called heat radiation or radiation heat transfer, is the transfer of energy from one object to another through electromagnetic waves without the need for any medium or contact between the two objects. The energy transfer occurs through the emission of electromagnetic waves, such as infrared radiation, by a warmer object and the absorption of these waves by a cooler object.
Heat transfer by radiation, abbreviated as \(Q_r\) or \(\phi\) (Greek symbol phi), also called heat radiation or radiation heat transfer, is the transfer of energy from one object to another through electromagnetic waves without the need for any medium or contact between the two objects. The energy transfer occurs through the emission of electromagnetic waves, such as infrared radiation, by a warmer object and the absorption of these waves by a cooler object.
Heat Transfer by Radiation Formula |
||
| \( Q_r \;=\; \epsilon \cdot \sigma \cdot A \cdot ( T_s^4 - T_\infty^4 ) \) | ||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( Q_r \) = Heat Radiation | \(Btu\;/\;hr\) | \( W \) |
| \( \epsilon \) (Greek symbol epsilon) = Surface Emissivity | \( dimensionless \) | \( dimensionless \) |
| \( \sigma \) (Greek symbol sigma) = Stefan-Boltzmann Constant | \(Btu\;/\;hr-ft^2-R^4\) | \(W\;/\;m^2-K^4\) |
| \( A \) = Surface Area | \( in^3 \) | \( mm^3 \) |
| \( T_s \) = Surface Temperature | \(^\circ R \) | \(^\circ K \) |
| \( T_\infty \) = Environmental Temperature | \(^\circ R \) | \(^\circ K \) |
Radiation is the primary mode of heat transfer in the vacuum of space, where there is no air or other matter to conduct or convect heat. Examples of heat transfer by radiation include the warmth of the sun's rays felt on the skin, the heat radiated from a fire, or the warmth felt from a hot object held near the face. The transfer of thermal energy can occur through three modes of heat transfer: conduction, convection, and radiation.

