Recombination
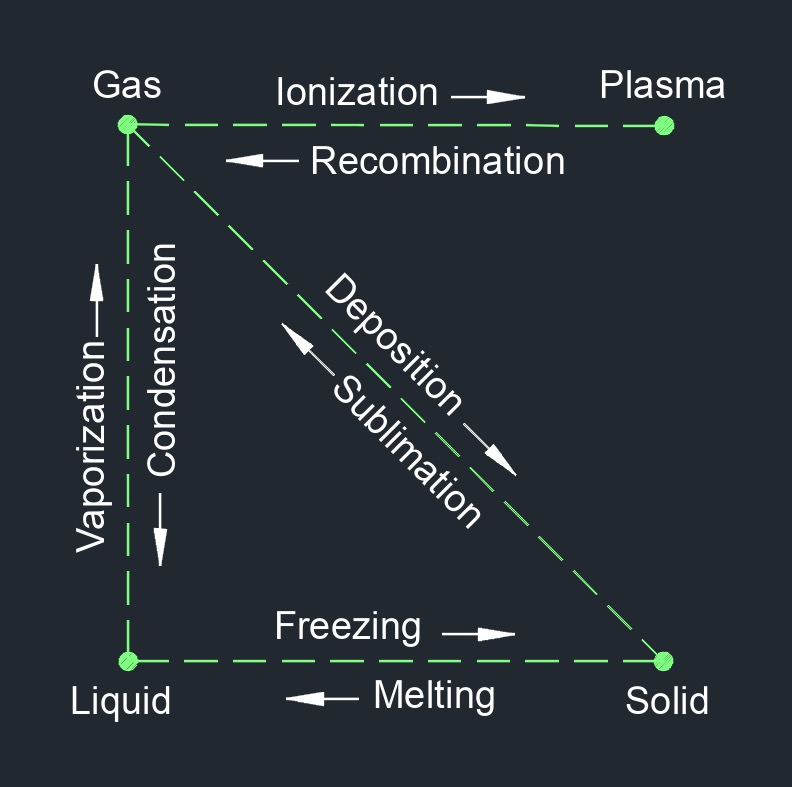
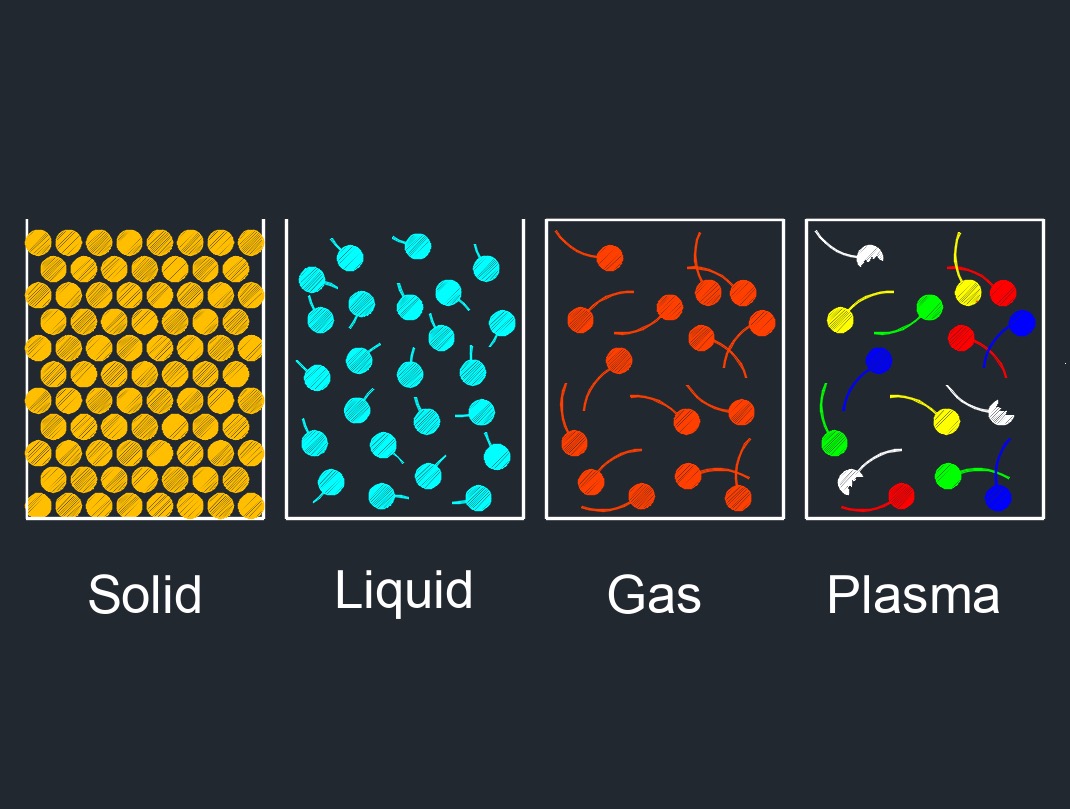 Recombination is a process in which charged particles, such as ions or electrons, combine to form neutral atoms or molecules. This process can occur in various contexts such as in the atmosphere, in plasmas, and in semiconductors. In the atmosphere, recombination occurs when a positively charged ion and a negatively charged electron come together to form a neutral molecule or atom. This process plays a role in the chemistry of the atmosphere, as it determines the concentrations of various molecules such as ozone and nitrogen oxides.
Recombination is a process in which charged particles, such as ions or electrons, combine to form neutral atoms or molecules. This process can occur in various contexts such as in the atmosphere, in plasmas, and in semiconductors. In the atmosphere, recombination occurs when a positively charged ion and a negatively charged electron come together to form a neutral molecule or atom. This process plays a role in the chemistry of the atmosphere, as it determines the concentrations of various molecules such as ozone and nitrogen oxides.
In plasmas, recombination occurs when free electrons and ions combine to form neutral atoms or molecules. This process can have important effects on the behavior of plasmas, such as in the operation of plasma devices and in fusion reactions. In semiconductors, recombination refers to the process by which charge carriers, such as electrons and holes, combine and neutralize each other, resulting in the loss of electrical conductivity. This process can limit the efficiency of semiconductor devices such as solar cells and light emitting diodes.
Recombination is an important process in many fields of science and engineering, as it plays a role in determining the behavior of charged particles and the properties of materials. Understanding and controlling recombination is therefore essential for developing new technologies and applications.

