Law of Conservation of Energy
Law of Conservation of Energy Formulas |
||
|
\( ( \frac{1}{2} \cdot m_f \cdot v_f^2 )+( m_f \cdot g_f \cdot h_f^2) \;=\; (\frac{1}{2} \cdot m_i \cdot v_i^2 ) + ( m_i \cdot g_i \cdot h_i^2 ) \) \( KE_f + PE_f \;=\; KE_i + PE_i \) |
||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( g \) = Gravity | \(ft\;/\;sec^2\) | \(m\;/\;s^2\) |
| \( h \) = Height | \(ft\) | \(m\) |
| \( m \) = Mass | \(lbm\) | \(kg\) |
| \( v \) = Velocity | \(ft\;/\;sec\) | \(m\;/\;s\) |
| \( KE \) = Kinetic Energy | \(bf-ft \) | \(J\) |
| \( PE \) = Potential Energy | \(lbf-ft \) | \(J\) |
| \( f \) = Final | - | - |
| \( i \) = Initial | - | - |
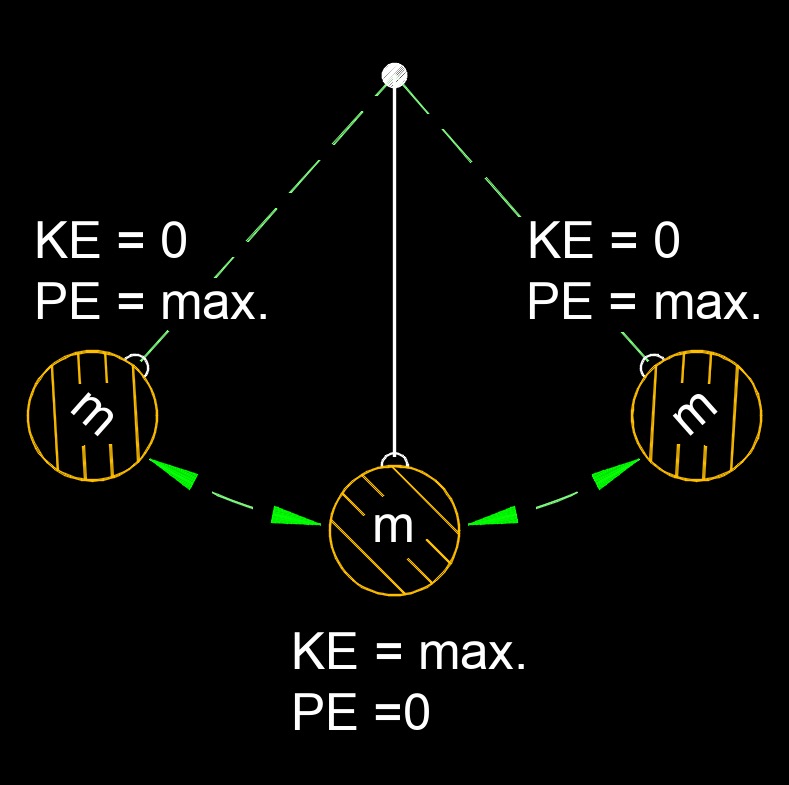 Law of conservation of energy, also called conservation of energy, states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, but may be changed from one form to another. This means that the total energy in an isolated system remains constant over time.
Law of conservation of energy, also called conservation of energy, states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, but may be changed from one form to another. This means that the total energy in an isolated system remains constant over time.
Energy Types
- Chemical Energy
- Electrical Energy
- Internal Energy
- Kinetic Energy
- Mechanical Energy
- Potential Energy
- Rest Energy
- Spring Energy
- Thermal Energy
- Work Energy

