Cathodic Protection
Cathodic Protection, Electrical, Corrosion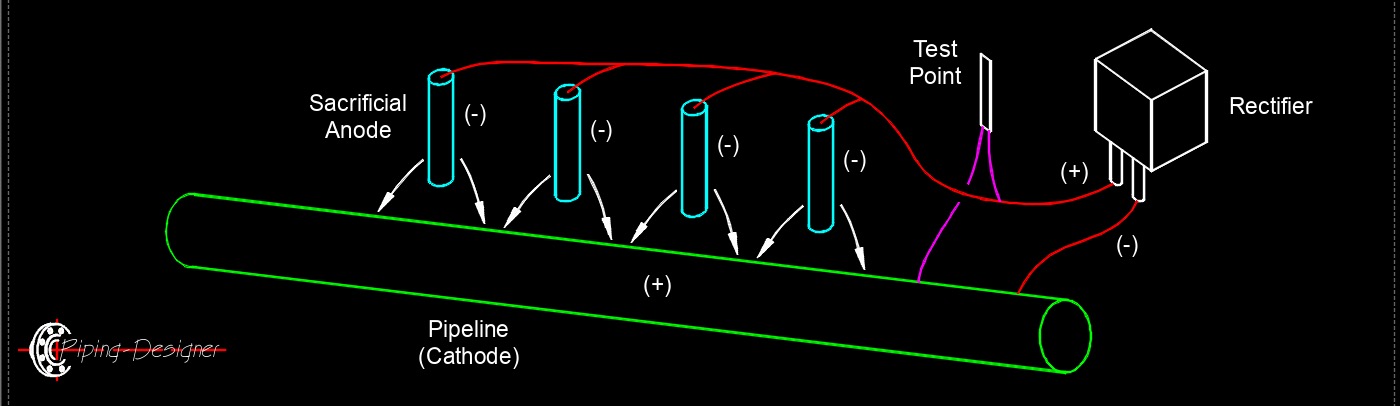 Cathodic protection, abbreviated as CP, is a technique used to prevent corrosion of metal structures and equipment by making them the cathode of an electrochemical cell. Corrosion occurs when metal is exposed to an electrolyte, such as water or soil, and a flow of electrons occurs between the metal and the electrolyte, resulting in the metal corroding. By making the metal structure the cathode of an electrochemical cell, the flow of electrons is reversed, and corrosion is prevented. CP is typically achieved by connecting a sacrificial anode made of a more active metal, such as zinc or magnesium, to the metal structure being protected. The sacrificial anode corrodes instead of the metal structure, providing cathodic protection. Another method of cathodic protection is impressed current cathodic protection, which involves using a direct current power source to provide the required current flow to the structure being protected.
Cathodic protection, abbreviated as CP, is a technique used to prevent corrosion of metal structures and equipment by making them the cathode of an electrochemical cell. Corrosion occurs when metal is exposed to an electrolyte, such as water or soil, and a flow of electrons occurs between the metal and the electrolyte, resulting in the metal corroding. By making the metal structure the cathode of an electrochemical cell, the flow of electrons is reversed, and corrosion is prevented. CP is typically achieved by connecting a sacrificial anode made of a more active metal, such as zinc or magnesium, to the metal structure being protected. The sacrificial anode corrodes instead of the metal structure, providing cathodic protection. Another method of cathodic protection is impressed current cathodic protection, which involves using a direct current power source to provide the required current flow to the structure being protected.
| Engineering |
| Chemical Engineering |
CP is commonly used in a variety of industries, including oil and gas, marine, and transportation, to protect metal structures such as pipelines, tanks, and ships from corrosion. It is a highly effective technique for preventing corrosion, and can extend the life of metal structures significantly. CP systems require regular monitoring and maintenance to ensure that they continue to function properly over time. Corrosion engineers and technicians are responsible for designing, installing, and maintaining cathodic protection systems to ensure that metal structures remain protected from corrosion.
- See Article - Cathodic Protection Glossary
Cathodic Protection Anode Types

